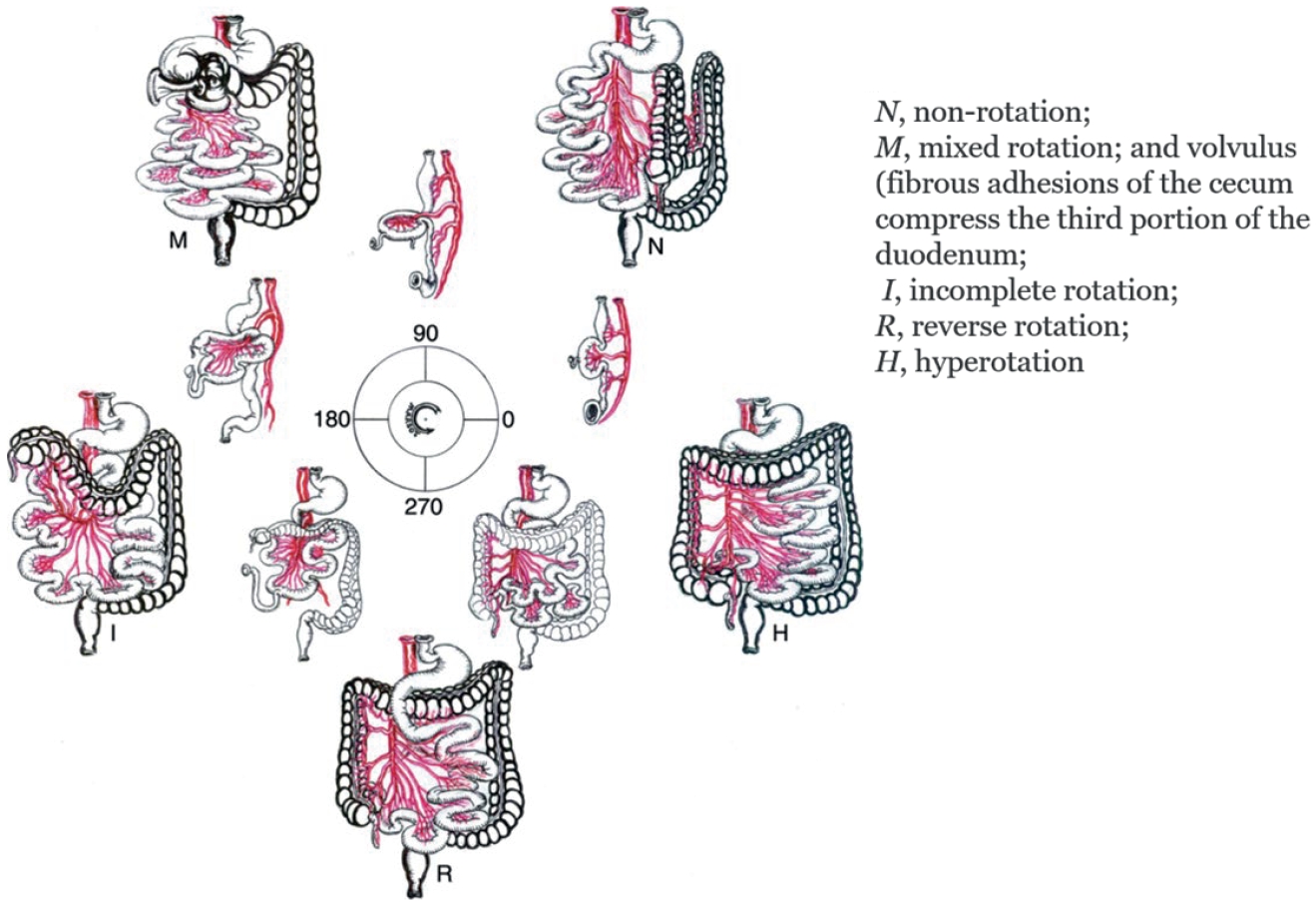
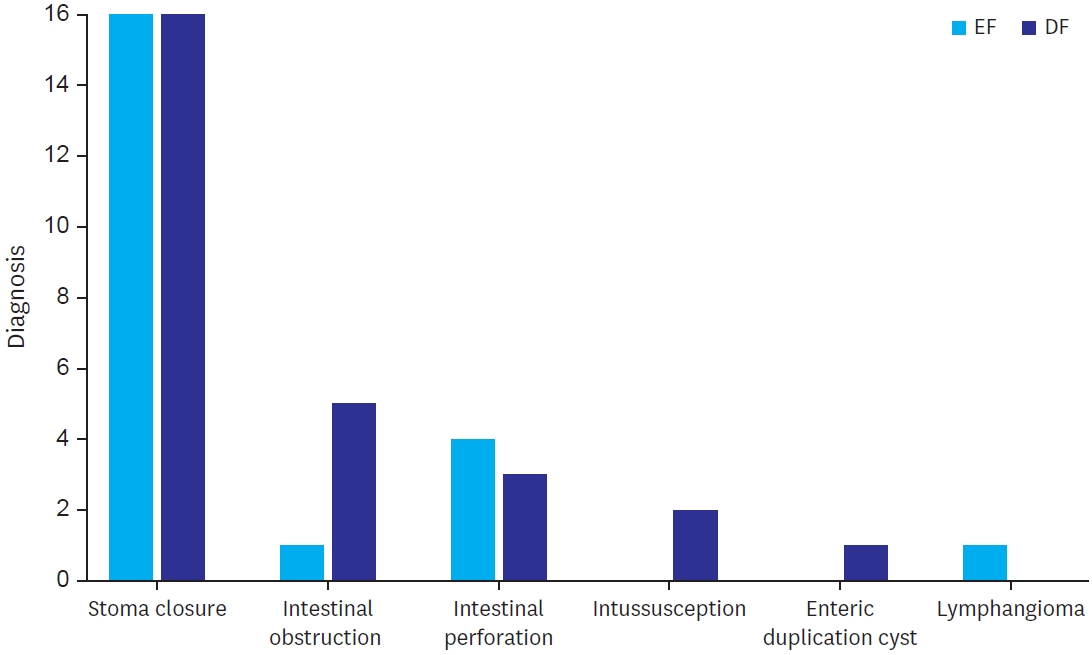
Citations

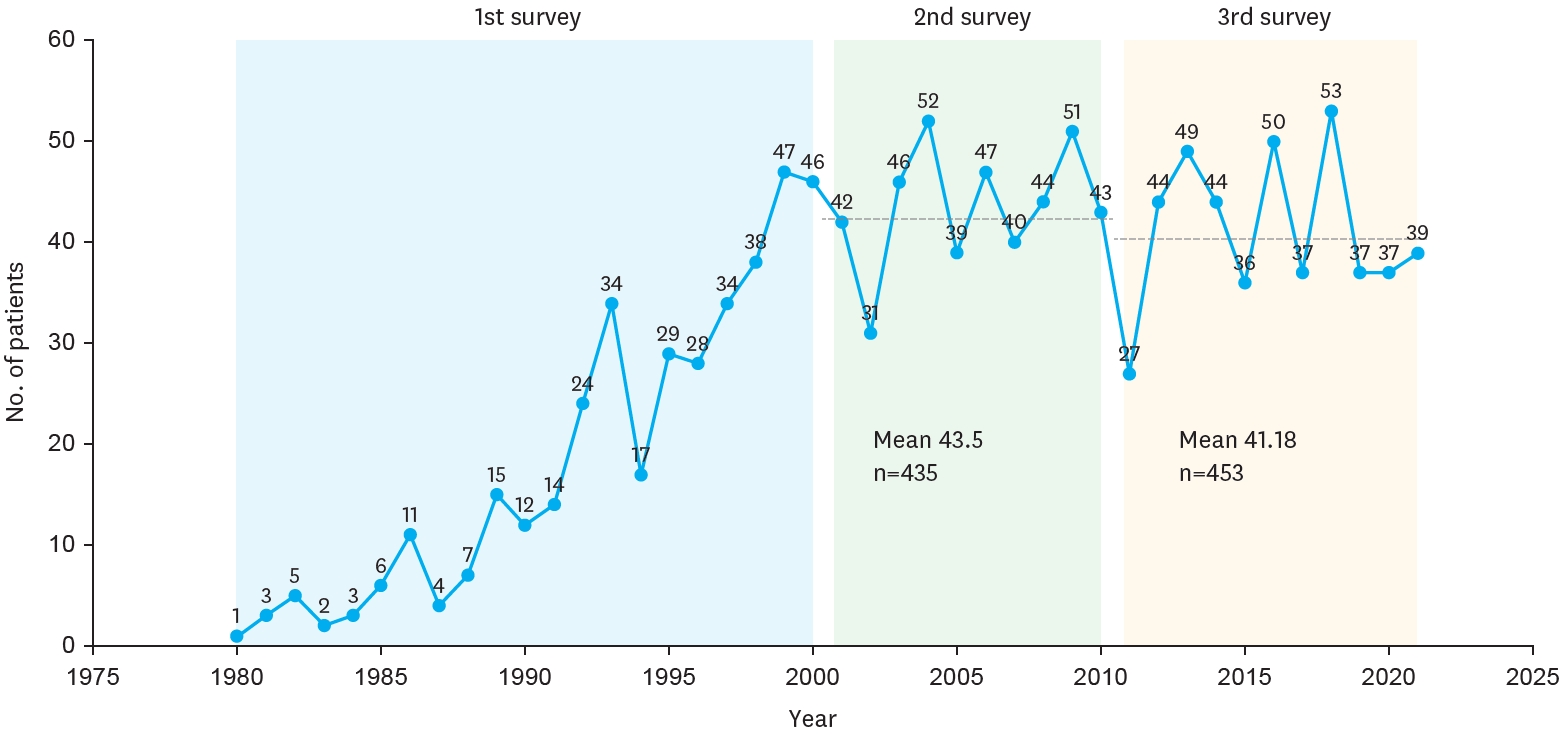
Citations

The Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons (KAPS) performed a nationwide survey on sacrococcygeal teratoma in 2018.
The authors reviewed and analyzed the clinical data of patients who had been treated for sacrococcygeal teratoma by KAPS members from 2008 to 2017.
A total of 189 patients from 18 institutes were registered for the study, which was the first national survey of this disease dealing with a large number of patients in Korea. The results were discussed at the 34th annual meeting of KAPS, which was held in Jeonju on June 21–22, 2018.
We believe that this study could be utilized as a guideline for the treatment of sacrococcygeal teratoma to diminish pediatric surgeons' difficulties in treating this disease and thus lead to better outcomes.
Citations

This study aimed to compare the outcomes of open fundoplication (OF) and laparoscopic fundoplication (LF) in children with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
We retrospectively reviewed the electronic medical charts of pediatric patients who underwent fundoplication for GERD between January 2005 and May 2018 at the Korean tertiary hospital. Patient characteristics, operation type, associated diagnosis, operation history, neurologic impairment, postoperative complication, recurrence, and operation outcomes were investigated. The Mann-Whitney U test or Student's t-test was used to evaluate continuous data as appropriate. The χ2 test was used to analyze categorical data.
A total of 92 patients were included in this study; 50 were male and 42 were female. Forty-eight patients underwent OF and 44 patients underwent LF. Patient characteristics, such as sex ratio, gestational age, symptoms, neurological impairment, and history of the previous operation were not different between the two groups. A longer operative time (113.0±56.0 vs. 135.1±49.1 minutes, p=0.048) was noted for LF. There was no significant difference in operation time when the diagnosis was limited to only GERD, excluding patients with other combined diseases. Other surgical outcomes, such as intraoperative blood loss, transfusion rate, hospital stay, and recurrence rate were not significantly different between the 2 groups. The complication rate was slightly higher in the OF group than in the LF group; however, the difference was not significant (20.8% vs. 11.4%, p=0.344).
LF is as safe, feasible, and effective as OF for the surgical treatment of GERD in children.
Congenital milia of the nipple are extremely rare, and standard treatment has not yet been established because nipple preserving excision is problematic due to the location. Although most reports show excisional biopsy resulting in good outcomes without recurrence, there is a lack of consensus about treatment modality, with several studies suggesting that incisional evacuation by needle, or a ‘wait and see’ approach represent sufficient treatment. This case report is about a recurrent case after incisional evacuation for congenital milium of the nipple. We recommend nipple preserving excision with exfoliation of the milial capsule as being the most appropriate treatment modality for congenital milium of the nipple.
Lymphatic malformations (LMs) are congenital malformations of the lymphatic system which can be effectively treated by sclerotherapy. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of doxycycline in the treatment of LMs.
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of all patients who were diagnosed as LMs and underwent doxycycline sclerotherapy in Asan Medical Center between March 2013 and February 2014. Thirty-five sclerotherapy procedures were performed on 21 patients. The procedures were performed under general anesthesia. After each treatment, the clinical and radiographic response was characterized as complete (≥80% decrease in lesion size), partial (<80% decrease of size), or no response (no decrease of size).
There were 11 male patients and 10 female patients. The median age of sclerotherapy was 21 months (range, 2–180 months). The most common location was cervicofacial (52.3%), followed by extremity (28.6%) and truncal (19.0%). The most common lesion type was macrocystic (71.4%), followed by microcystic (28.5%). There was one (2.8%) skin necrosis which was recovered by wound management. Thirty-eight percent of patients had a complete response, 47.6% of patients had a partial response and 14.3% of patients had no response. Median frequency of treatment was one (range, 1–5). No response group consisted of all microcystic type.
Sclerotherapy with Doxycycline is safe and effective for macrocystic LMs.
Citations

Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is associated with consumption of under cooked gound beef, characterized by triad of renal failure, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia. Early recognition of this disease, maintenance of fluid balance and proper dialysis seems to prevent acute mortality. A 23-month-old boy was admitted with abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea and fever. On hospital day (HD) #2, he developed aggravated abdominal pain compared to the initial assessment. Contrast abdominal computed tomography demonstrated findings suggestive acute appendicitis so the patient was underwent laparoscopic appendectomy. On HD #3 and #4, his laboratory findings showed marked thrombocytopenia and serum creatinine elevation. He was transferred to another hospital for dialysis with the impression of acute renal failure. Later, verotoxin-producing
Undescended testis (UDT) is a developmental defect in which one or both testicles do not arrive in the scrotum. Its prevalence at birth and one year after is 2%–4% and less than 1%, respectively. Currently, surgery is recommended to treat congenital cryptorchidism in order to prevent testicular degeneration. Classic method is performed via incision in inguinal and scrotum and the new method is done via incision in scrotum.
Sixty male participants with 65 UDT undergoing surgery were randomly assigned to scrotal incision (n=31) and classic inguinal incision methods (n=34). Patients were followed for 6 months and testicular atrophy, infection, recurrence, and duration of surgery were compared between two groups.
Scrotal incision compared to classic incision method had significantly lower duration of surgery (19.06±2.96 minutes vs. 30±10.42 minutes; p=0.002) and recurrence during follow-up (0 vs. 5 cases; p=0.026). There was only one surgical site infection in the scrotal incision method. There were hematoma and post-operative swelling in 13.3% of cases after scrotal incision method.
Scrotal incision is an alternative method for the UDT with lower duration of surgery, lower recurrence rate, and better cosmetic results.
Citations

Although nonoperative treatment of appendicitis (NOTA) in the pediatric population has been well reported recently, patient selection and treatment scheme varies among studies, making it difficult to establish treatment standards for NOTA.
In a single medical center, patients younger than 18 years who were diagnosed with appendicitis: 1) with abdominal pain not exceeding 24 hours, 2) without radiologic evidence of appendicolith or appendiceal perforation or pelvic abscess, and 3) without signs of frank generalized peritonitis were offered NOTA, and their data were prospectively collected.
Twenty-two patients with uncomplicated appendicitis agreed to NOTA and were enrolled in the study. The initial success rate (resolution of abdominal pain and hospital discharge without appendectomy) was 100% (22 out of 22 patients). At a median follow-up period of 23.8 months, two patients had recurrence at two and three months after completion of NOTA. These patients underwent laparoscopic appendectomy.
Stringent patient selection may be necessary to apply NOTA safely for all children with uncomplicated appendicitis. Further studies concerning patient selection and conformed treatment protocols for NOTA are required.
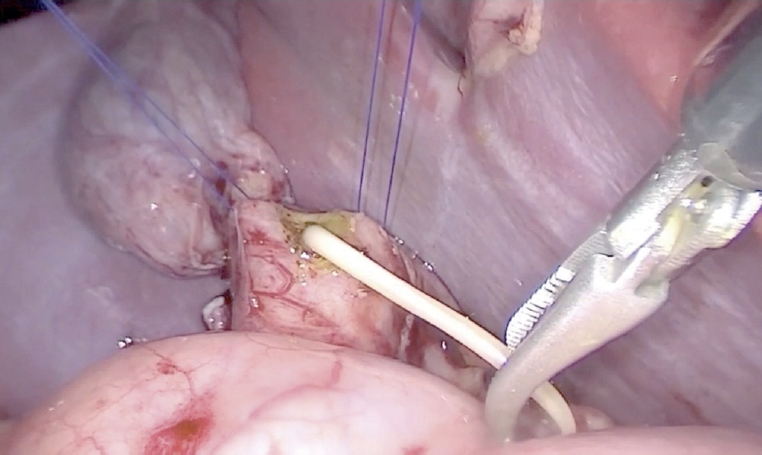
Esophageal atresia (EA) is a diverse disease entity. We present a case of long gap EA without fistula corrected through totally laparoscopic and thoracoscopic esophageal replacement using gastric tube. A male baby weighing 3,000 g, with suspicion of EA, was born at gestational age of 37+6 weeks. Gastrostomy was made at an age of two days; seven months later, definite operation was planned. We determined to perform the gastric tube replacement due to long gap revealed by fluoroscopy. Gastric mobilization, gastric tube formation, and pyloroplasty were performed laparoscopically. An isoperistaltic 9 cm gastric tube was made using 2 Endo GIA 45, and interrupted end-to-end esophago-esophagostomy was performed thoracoscopically. With laparoscopy, gastropexy to the diaphragm was performed through the interrupted suture. Operation time was 370 minutes; there was no intraoperative event. Postoperative course was uneventful. He underwent esophageal balloon dilatation due to anastomosis stenosis in the months after surgery.
Congenital absence/hypoplasia/fusion of ribs are very rare anomalies and presentation varies from asymptomatic to life-threatening. Visibly evident cases are straightforward to diagnose but this is not always the case. Familiarity and awareness of these anomalies can help to diagnose cases with subtle signs and symptoms. Proper radiological investigations are vital for anatomical delineation. Absence or hypoplasia of the inferior ribs along with its attached muscles can cause ‘lung hernia’ that produces an unstable chest leading to paradoxical respiratory movements. Here, we present a case of hypoplastic and fused ribs in an infant, who presented with respiratory distress and created a diagnostic dilemma.
Citations

The introduction of Malone antegrade continence enema) in the management of children with fecal incontinence has brought remarkable improvement in patient care, Malone originally described appendix as a conduit and it has become widely accepted. However, surgeons are faced with situations where appendix is not available, the selection and creation of other conduit is always a challenge. We present our technique and experience with the use of alternative catheterizable conduits for antegrade continence enema (ACE).
Retrospective review of children who underwent ACE procedure in our institution from March 2009 to January 2014. The details retrieved: indication, reason for non availability of appendix, type of conduit, complications and patient's satisfaction.
Five children were identified in whom the appendix was not available or suitable. In four children cecal/colon-based flap was used and in one child, ileal (Monti) segment was used to create a conduit. The mean follow-up was 3.2 years. All patients were satisfied with the procedure and no stenosis or loss of conduit was noted in the follow-up.
Continent catheterizable conduit for ACE can be accomplished with transverse tubularized intestinal segments and cecal/colonic flaps, with excellent outcome, irrespective of tissue used. Surgeon's preference and the patient's peculiar anatomy should determine the surgical technique to be used.
The risk of acute abdomen in neonates and infants is generally increased due to advanced maternal age and neonatal intensive care unit care development. Enterostomy is a safe procedure for acute abdomen in neonates and infants. However, there is no consensus for the optimal timing of enterostomy closure (EC). A few considerations should be reviewed for deciding the timing of stoma closure to obtain the best outcome. Distal loopography is commonly performed upon examination to ascertain the existence of a distal passage after EC, detect signs of disease-specific complications, and assess the need of surgery in addition to EC. Pathology review is also one important pre-closure consideration. When the incidence of a hypoganglionosis or an aganglionosis combined with acute abdomen is observed in neonates and infants, thorough examinations should be performed to conclusively determine whether there is no passage disturbance of the distal bowel. Refeeding not only provides information about chance to grow, electrolyte imbalance correction, and proximal and distal bowel size match, but also provides information about distal bowel passage when there is a doubtful distal loopography or pathology result. Early closure enables growth spurt with the correction of water/electrolyte imbalance. It potentially reduced medical costs, less discrepancy between proximal and distal bowel size. Some factors favoring a late stoma closure may be due to less postoperative complications, early recovery, shorter time of total parenteral nutrition after EC, and decreased length of hospitalization after the EC. Some studies have shown controversial results. In summary, a pre-closure evaluation is imperative to assure the safety of an EC. The optimal timing of an EC remains controversial. For this reason, individualized approach is needed after reviewing the general condition of each patient. Further prospective study on optimal timing of stoma closure including a randomized clinical trial is needed.
Citations

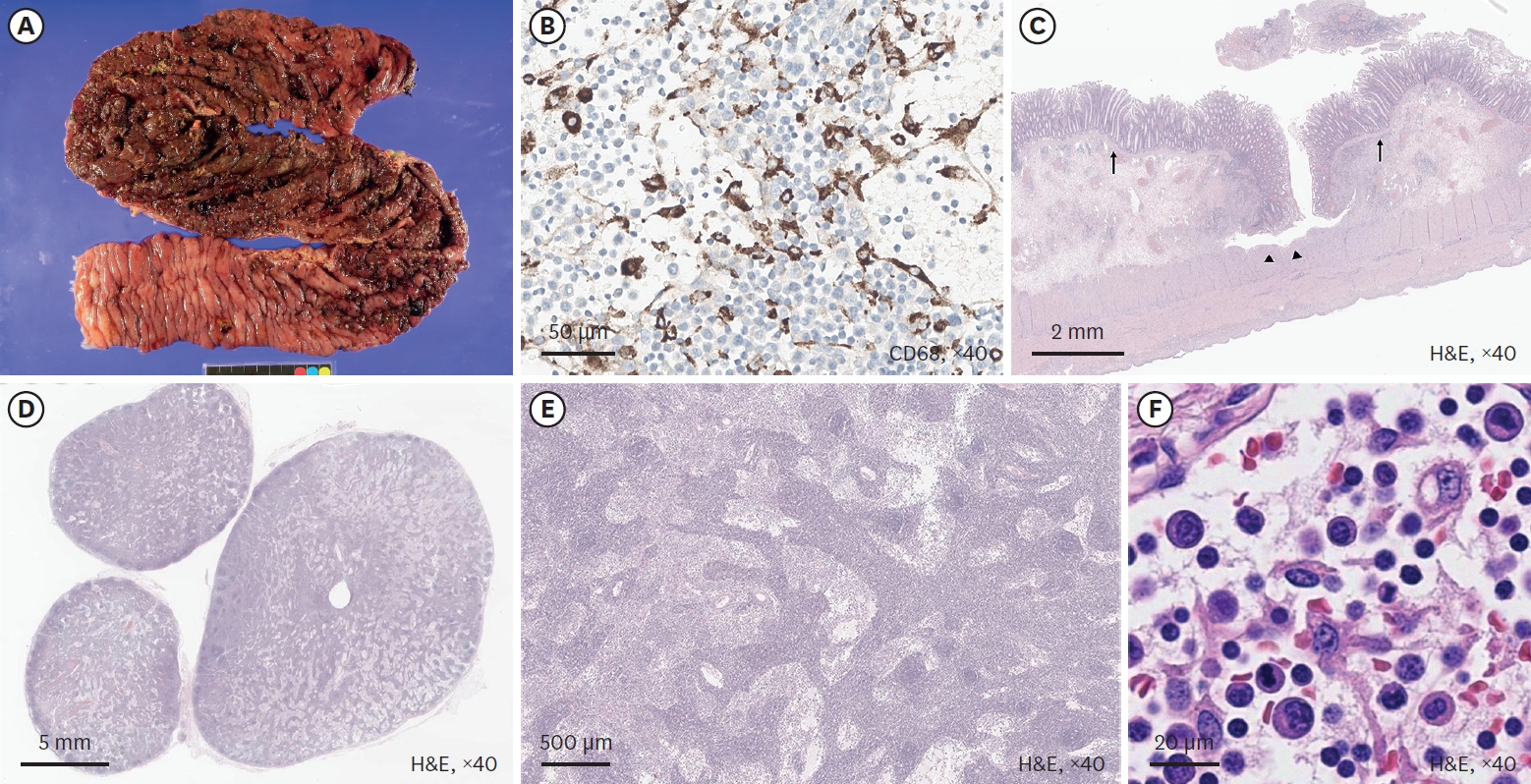
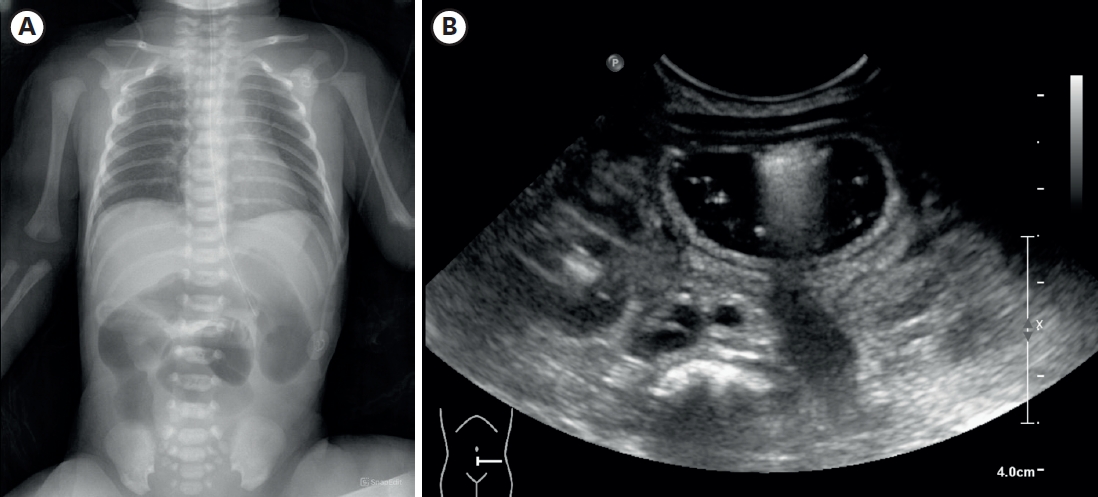
Lymphatic malformations are benign congenital malformations of the lymphatic system that occur predominantly in children. Most lymphatic malformations occur in the head and neck region, with those in abdominal locations, such as the mesentery, omentum and retroperitoneum, being less common, accounting for fewer than 5% of lymphatic malformations in children. This study analyzed the clinicopathologic characteristics and treatment outcomes of abdominal lymphatic malformations in children.
The medical records of 12 pediatric patients treated for abdominal lymphatic malformations at our institution between April 1999 and September 2017 were retrospectively reviewed. Demographic and clinical characteristics, including gender, age, symptoms and signs, diagnostic modalities, and treatment results, were analyzed.
The 12 patients included 11 boys and 1 girl, ranging in age from 3 months to 17 years (median 36.5 months) at presentation. The primary signs and symptoms included abdominal pain, abdominal mass and abdominal distention. Other symptoms and signs included fever, vomiting, scrotal pain and mass, and right inguinal mass. All patients were diagnosed by abdominal ultrasonography and computed tomography, and all underwent surgical excision with or without bowel resection. The lymphatic malformations occurred in the retroperitoneum (n=4), omentum (n=4), jejunal mesentery (n=2), and retroperitoneum and mesentery (n=2). Seven patients underwent complete mass excision, including 3 who underwent laparoscopic excisions, and 3 who underwent mass excision with segmental resection of the adjoining bowel. Two patients underwent incomplete excision because the lesion was extensive and invaded the superior mesenteric vessels. There was no major perioperative morbidity in any patient. At a median follow-up of 50 months (range, 8–183 months), only 1 patient experienced recurrence.
Although abdominal lymphatic malformations are benign, most children present with acute abdominal symptoms, necessitating early surgical treatment.
Citations

Early suspicion is essential in diagnosing pyriform sinus cysts. We report two neonatal cases of pyriform sinus cysts presented as neck masses. The first case presented as a right neck mass, which made it more difficult to suspect a pyriform sinus cyst considering the prevalence of left sided cysts. Surgical resection was done in both cases and anatomical investigation suggested both to originate from the fourth branchial pouch. Detection of air bubble containing mass on imaging studies can aid early diagnosis and early use of gastric tube feeding can facilitate treatment by preventing milk contamination which may result in infection of the sinus cyst.
Citations

We evaluated perioperative and long-term outcomes of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) and established indications of MIS in solid pseudopapillary tumor (SPT) in pediatric patients.
From October 1992 to April 2018, 66 patients (age, <18 years) diagnosed with SPT underwent either open pancreatectomy (OP) or MIS. Variables including postoperative complications and recurrence rates were retrospectively analyzed.
Thirty-five patients underwent open surgery and 31 underwent laparoscopic/robotic surgery. Mean tumor size in MIS was significantly smaller than that in OP (4.3±1.8 cm vs. 7.6±3.5 cm, p=0.005). There were 4 cases of open conversion from laparoscopic surgery because of vessel encasements (n=2), bleeding (n=1), and pancreatic ductal injury (n=1). Solitary pseudopapillary carcinoma was diagnosed in 6 patients. Recurrence was observed in 3 and 1 patients who underwent OP and MIS, respectively (p=0.634). Tumor size, mass size/abdominal diameter (MS/AD) ratio, and degree of the portal or superior mesenteric vein involvement were the most important indications for MIS.
MIS is being widely used in pediatric surgeries with increased expertise and safety, especially in pancreatic diseases. Careful patient selection for MIS in regards with parameters such as MS/AD ratio and vessel abutment might be a feasible choice.
Citations

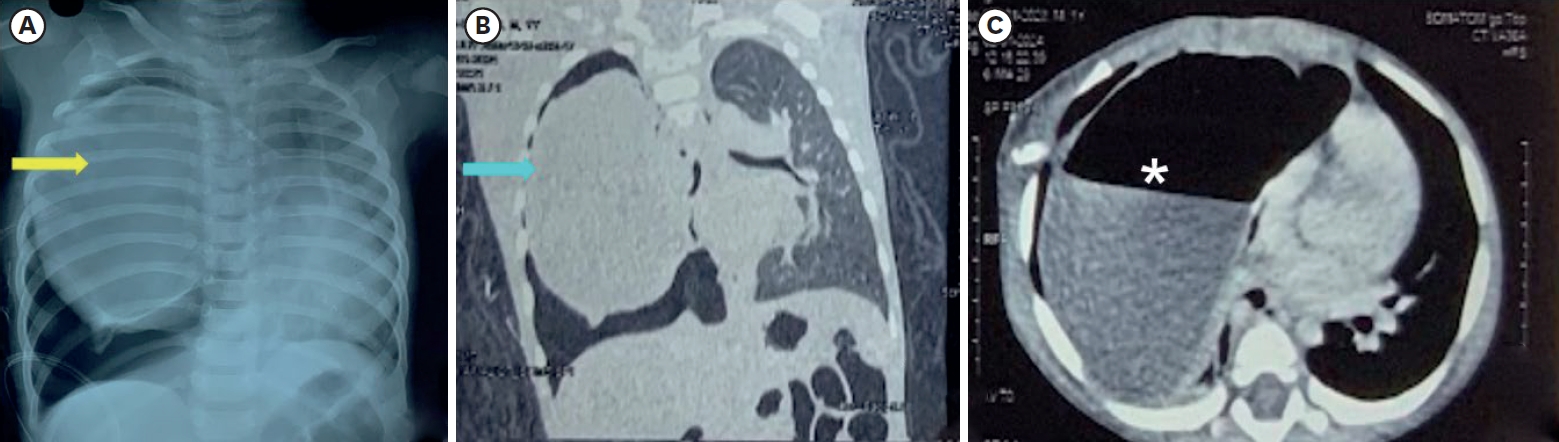
Although gallbladder (GB) hydrops in childhood is uncommon, it is most commonly associated with Kawasaki disease (KD) and can be a risk factor of poor outcomes in patients with KD. Our patient presented with a fever, diffuse abdominal pain, maculopapular rash, bilateral conjunctivitis, red and fissured lip tissue, and 3 days of right cervical swelling. Abdominal examination revealed abdominal distension and tenderness. Abdominal ultrasonography was performed to identify the source of abdominal symptoms, which revealed dilatation of the GB. Abdominal computed tomography scan was also performed to exclude other hepatobiliary disease, which showed normal hepatobiliary systems. The GB of our patients returned to a normal size without any complications, but it regressed very slowly. We report a case of a 6-year-old boy with KD who presented with markedly distended and unusually prolonged GB hydrops.
Citations

This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between nutritional support and growth velocity after abdominal surgery in neonates.
The electronic medical records of 45 neonates who underwent abdominal surgery in neonatal intensive care unit from 2012 to 2016 were collected to see how surgery and postoperative nutrition affect for the growth of neonate with abdominal surgery. The growth velocity was measured from the time of surgery to the time of discharge based on body weight.
In neonates who achieve their protein requirement on the first day after surgery, the growth velocity was better than that in neonates who did not achieve their protein requirement on the first day after surgery (4.31 vs. 15.21; p=0.004). Based on the type of surgery, length of bowel resection and surgical complications, this study showed better growth velocity in neonates who had no surgical complications (5.34 vs. 12.74; p=0.775), reoperation (5.25 vs. 22.19, p=0.987), or bowel resection (6.79 vs. 9.95, p=0.302). However, there was no statistically significant difference among these factors.
We concluded in this study that adequate protein supplement from the first day of surgery could have a positive effect on the growth velocity of neonates who underwent abdominal surgery.
We describe our experience in managing congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) in neonates.
From February 1995 to July 2014, 64 neonates diagnosed with CDH were managed. The medical records of these neonates were retrospectively reviewed.
There were 40 males and 24 females. CDH was on the left side in 44 cases (68.8%), on the right side in 19 cases (29.7%) and bilateral in 1 case (1.6%). Forty-six patients (71.9%) received surgical repair of the hernia while 18 patients (28.1%) died prior to surgery. The timing of surgery was mean 7.0 days after birth. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was used in six patients (9.4%), High-frequency oscillation ventilation was used in 49 patients (76.6%), and nitric oxide was used in 42 patients (65.6%). Thirty-three cases (71.7%) of CDH repair were done via open laparotomy, 3 cases (6.6%) by open thoracotomy. and minimally invasive thoracoscopic repair was done in 10 cases (21.7%). Ten cases (21.8%) required patch repair of the CDH. Barotrauma and pneumothorax of the contralateral lung was seen in 16 cases, leading to death in 15 of these cases. The overall survival rate was 48.4% (31/64) and postoperative survival rate was 67.4% (31/46). When all patients are divided into 3 groups by era and analyzed by logistic regression models, the mortality outcome of recent era (2009–2014) was significantly better than that of intermediate era (2002–2008) (29% vs. 71%, p=0.006) and tended to be better than that of past era (1995–2001) (42% vs. 71%, p=0.062).
The overall survival of neonates with CDH at our center has improved over the last two decades. Sixty-four neonates with CDH were managed at a single center and their overall survival was 48.4%. The risk factors for mortality include the occurrence of pneumothorax and right side lesions.
Citations

We present an extremely rare case with double H-type tracheoesophageal fistulae identified with a time-lapse and repaired separately. A newborn male presented with cyanosis after breastfeeding. Contrast esophagogram demonstrated an H-type fistula, and then it was repaired in a standard fashion via right thoracotomy. When routine esophagogram was taken on postoperative day 10, another fistula was noticed at a level higher than the previous one. Bronchoscopy was performed to evaluate the lesion whether it was a recurred fistula or a second H-type fistula. However, it was so tiny that it was not visible with bronchoscopy. It was discovered only two months later when the fistula had grown up with the baby. The second H-type fistula was repaired through a cervical incision. Although double H-type fistulae are extremely rare, the possibility of another fistula, as well as recurrence, must be ruled out when symptom recurs after a definitive operation of an H-type fistula.
Citations

Single-port laparoscopy-assisted surgery is being performed for various operations in pediatric patients recently. The aims of this study were to prove the safety and find well-matched indications of small bowel resection using single-site umbilical laparoscopic surgery (SSULS).
From 2011 to 2016, 29 pediatric patients underwent SSULS. Medical records were retrospectively reviewed.
A total of 29 patients were included and 30 SSULS were performed in this study. The mean age at operation was 5.7 years, and the mean weight was 21.9 kg. Meckel's diverticulum was the most common indication for SSULS, followed by small bowel intussusception due to leading point mass, small bowel duplication, and Crohn's disease. In most cases, estimated blood loss was negligible except in Crohn's disease with severe inflammation. While answering post-discharge questions about scars, most parents responded that they were satisfied with the postoperative wound.
SSULS is a useful operation to try even for surgeons who do not have advanced laparoscopic skills. Complication rates of single-port operations do not differ from those of conventional laparoscopic operations. Most lesions of the small bowel could be indications of SSULS. Careful attention is required when performing SSULS in patients with Crohn's disease.
Citations

Total proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (T-IPAA) in childhood is a surgical procedure mainly applied to familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or ulcerative colitis (UC), but it can be applied to non-FAP/non-UC disease (NFNU). Studies regarding the role of T-IPAA who underwent the operation in childhood, especially in terms of long-term gastrointestinal function, complications, and quality of life (QOL) are limited. The aim of this study was to evaluate the characteristics of patients receiving T-IPAA and to compare their bowel function outcomes and QOL.
Patients aged ≤18 years at the time of T-IPAA were included. Their medical records were retrospectively reviewed. Krickenbeck classification, Cleveland Clinic Incontinence (CCI) score, 36-item Short-form Health Survey Questionnaire, and Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index were used for the evaluation of bowel function and QOL. The median follow-up period was 9.8 years.
Of the 25 patients, 9 had FAP, 9 had UC, and 7 had NFNU. NFNU include 3 of Hirschsprung disease, 2 of intestinal neuronal dysplasia, and 2 of imperforate anus. The median age at T-IPAA was 17.8, 14.2, and 9.3 years for FAP, UC, and NFNU, respectively (p=0.001). Bowel function was satisfactory in terms of voluntary bowel movement (VBM), soiling, and constipation. VBM and constipation were not different between the groups, but soiling was most in NFNU (100%, p=0.047). However, QOL was best in the NFNU group in surveys (p=0.034 and 0.004, respectively).
T-IPAA could be safely applied not only for FAP and UC but also for other diseases in selective cases, with caution.
Citations

Preoperative ultrasonography (USG) in pediatric inguinal hernia has controversy. In this study, we analyzed the cases of pediatric inguinal hernia with/without preoperative USG and discussed whether USG is necessary.
We reviewed medical records of 1,441 patients who underwent inguinal hernia repair in Seoul National University Children's Hospital between January 2011 and August 2016 retrospectively.
Male were 69.3% and age at operation was 37.8±36.5 months old. There were 150 patients (10.4%) performed USG preoperatively. The department ordered to perform USG included department of surgery (n=71), emergency medicine (n=42), pediatrics (n=26), urology (n=10) and outside hospital (n=1). The reasons of performing USG included evaluation for hernia laterality (n=82), incarceration (n=28), testis (n=15), request of parents (n=14), scrotal mass (n=6) and incidentally found during evaluation for another disease (n=5). Excepting 5 cases of incidental finding, of 145 cases with USG, 12 (8.3%) cases changed the surgical plan; change to bilateral repair from unilateral repair (n=5), emergency operation due to incarceration (n=4) which include 1 salpingo-oophorectomy, 1 open abdomen surgery and 2 hernia repair after reduction of ovary, change to co-operation of orchiopexy (n=2) and change to laparoscopic surgery from open surgery due to herniation of both ovaries into one inguinal canal (n=1). In group without USG (n=1,291), 5 patients (0.4%) had unexpected problems during operation; 2 co-operation of orchiopexy because of transverse testicular ectopia (n=1) and right undescended testis (n=1), 2 hypertrophy of major labia and 1 retroperitoneal lymphangioma at inguinal area misdiagnosed as inguinal hernia.
It was difficult to interpret the meaning of preoperative USG because not all patients had performed it. In this study, 10.4% of patients performed USG and 8.3% of them changed surgical plan. About 0.4% of patients without preoperative USG would have benefited from it for surgery if they had performed it. Since the percentage is too low, it is unreasonable to conclude that USG has diagnostic utility in inguinal hernia in this study.
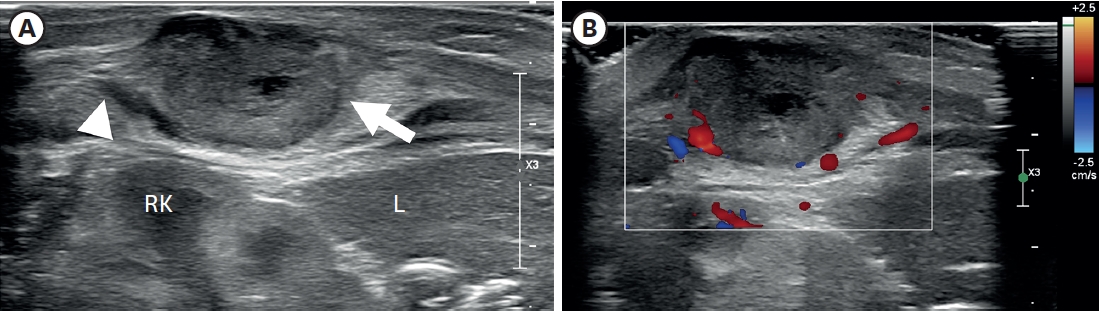
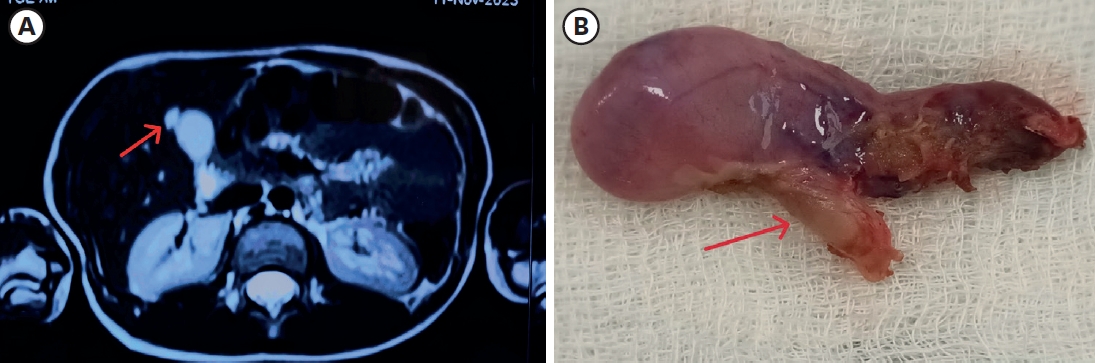
A 6-year-old male who lived with a mother in a single-parent family was referred to the emergency room with multiple traumas. There was no specific finding on CT scan of the other hospital performed 55 days before admission. However, CT scan at the time of admission showed common bile duct (CBD) stenosis, proximal biliary dilatation and bile lake formation at the segment II and III. Endoscopic retrograde biliary drainage was performed, but the tube had slipped off spontaneously 36 days later, and follow-up CT scan showed aggravated proximal biliary dilatation above the stricture site. He underwent excision of the CBD including the stricture site, and the bile duct was reconstructed with Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy. Pathologic report of the resected specimen revealed that the evidence of trauma as a cause of bile duct stricture. While non-iatrogenic extrahepatic biliary trauma is uncommon, a level of suspicion is necessary to identify injuries to the extrahepatic bile duct. The role of the physicians who treat the abused children should encompass being suspicious for potential abdominal injury as well as identifying visible injuries.
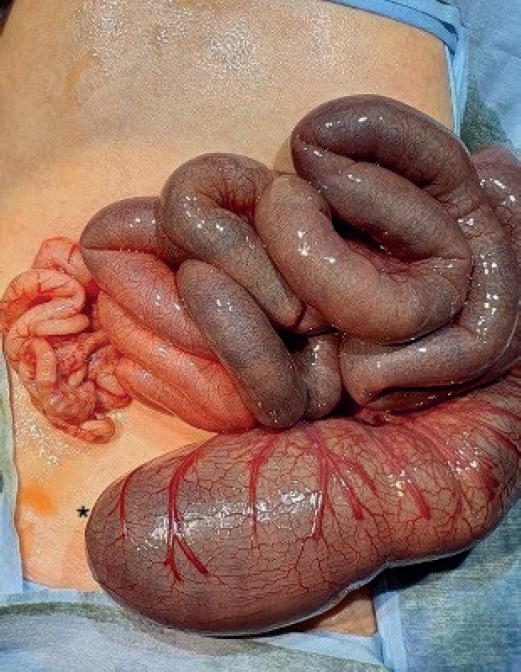
An 18-year-old male patient with cerebral palsy and scoliokyphosis came to the emergency department with abdominal distension and vomiting. He was a situs inversus patient with a feeding gastrostomy tube. Sigmoid volvulus was initially suspected, so rectal tube insertion and endoscopic decompression were attempted, but failed. So he went through explorative laparotomy, and transverse colonic adhesion and twisting around the gastrostomy tube and gastric wall was identified. Adhesiolysis and resection with redundant transverse colon and end-to-end colocolic anastomosis was performed. He discharged with symptom free. Suspecting transverse colonic volvulus is important when the patient has anatomical anomalies and feeding gastrostomy tube. Timely diagnosis with proper radiologic imaging should be made. Surgical resection of the redundant colon is needed for successful management of transverse colonic volvulus.
Citations

Santulli enterostomy has been used for various surgical abdominal conditions that require temporary diversion of bowel during a neonatal period. The aim of this study was to report clinical outcomes of Santulli enterostomy and to evaluate its usefulness.
Between January 2000 and December 2016, 40 neonates who underwent Santulli enterostomy were enrolled; Santulli enterostomies were performed for 25 patients without previous laparotomy (primary Santulli group) and 15 patients with previous laparotomy (secondary Santulli group).
Small bowel atresia is the first common indication of Santulli enterostomy (22/40, 55.0%), and luminal discrepancy between proximal and distal bowel was the most common determinant factor of Santulli enterostomy (17/40, 42.5%). The median age at surgery and mean birth weight were 2 days and 2,480 g respectively in the primary group, and 71 days, 2,340 g respectively in the secondary group. Operation time was significantly longer in the secondary group than the primary group (156±48 minutes vs. 224±95 minutes, p=0.019), and there was no difference in the time taken to initiation of oral feeding between the two groups. Santulli enterostomy closure was performed at median 65 days after Santulli enterostomy for primary group and 70 days for secondary group. Six complications (15.0%) were found after Santulli enterostomy, and nine complications (24.3%) after Santulli enterostomy closure (p=0.302). The incidence of complications was significantly higher in secondary group than in primary group (4.5% vs. 53.3%, p=0.001), and the reoperation rate was also significantly higher in the secondary group (4.5% vs. 46.7%, p=0.004).
Santulli enterostomy could be applied as a temporary enterostomy in neonatal patients with various surgical abdominal diseases. Considering the high complication rate after secondary Santulli enterostomy closure, decision making on the timing of enterostomy closure should be done with caution.
Citations

The management of lymphatic malformation (LM) in pediatric patients is challenging. Complete excision of LM is difficult to achieve in some cases. We reviewed our experience how to manage LM.
We retrospectively reviewed the patients who were treated for LM between 2010 and 2017. Medical records were reviewed about age of diagnosis, age of treatment age, gender, symptom, location of tumor, treatment modality, response and complication.
Sixty-three patients (39 boys and 24 girls) were included. Mean age at diagnosis was 14.5±28.0 months (range, neonate-10 years). The involved lesion were head and neck in 27 patients (42.9%), abdominal cavity in 7 patients (11.1%), chest wall and abdominal wall in 11 patients (17.5%), buttock in 7 patients (11.1%), and extremities in 11 patients (17.5%). The treatment options were including surgical resection in 32 patients, sclerotherapy in 7 patients, surgical resection combined sclerotherapy in 19 patients, and close observation in 5 patients. We achieved complete remission in 39 patients. Fourteen patients showed partial remission and 6 showed recurrences.
Despite surgical difficulty, meticulous excision with supportive treatment, and adjuvant sclerotherapy could get a favorable outcome without fatal complication. Decision should be based on surgeon's experience, location of LM, related symptoms, and consultation with patient's parents.
Citations

Barium enema is one of the diagnostic modalities for Hirschsprung'sdisease. The present study aimed to investigate the diagnostic accuracy of barium enema for Hirschsprung's disease, especially total colonic aganglionosis (TCA).
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of all the patients who were diagnosed as having TCA and underwent a barium enema in Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital between January 1998 and December 2016. All the tests were performed and reviewed by pediatric radiologists.
Among the total 19 patients with TCA who underwent barium enema, 9 patients (47.4%) had accurate radiographic results. Eight of the 13 neonate patients (61.5%) showed typical TCA radiological findings. However, only one of the 6 patients aged >4 weeks (16.7%) had accurate radiological diagnosis.
Barium enema showed low accuracy for TCA, and its diagnostic performance was better in neonatal period than in those aged >4 weeks.
Congenital esophageal stenosis (CES) is a rare disease that has been reported to occur once in every 25,000 to 50,000 births. According to its etiology, CES is divided into 3 subtypes, tracheobronchial remnants (TBR), fibromuscular hypertrophy (FMH) and membranous diaphragm (MD). Symptoms begin at the weaning period and the introduction of solid food around 6 months with dysphagia and vomiting. Esophagography is first screening test and endoscopic ultrasonography plays important roles to diagnose subtypes deciding therapeutic plan. TBRs were generally treated with surgical resection and end-to-end anasotomosis, whereas FMH and MD had good response rate to endoscopic or radiologic guided dilatation. This article reviews the literature on the etiology, clinical course, diagnosis and management of CES including recent opinion.

