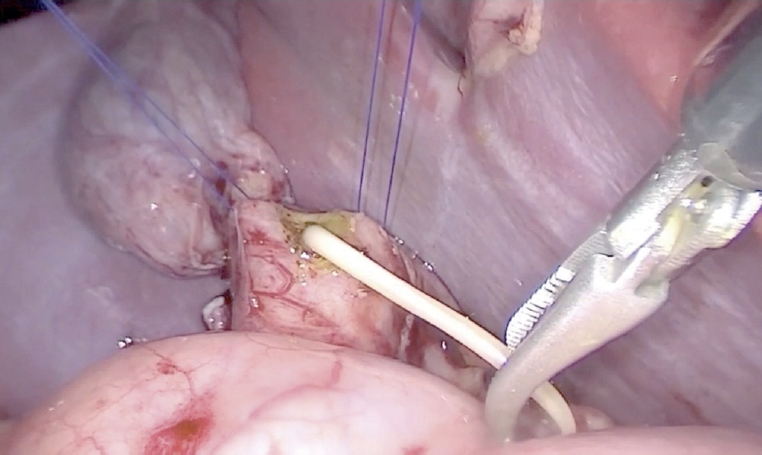
Esophageal atresia (EA) is a diverse disease entity. We present a case of long gap EA without fistula corrected through totally laparoscopic and thoracoscopic esophageal replacement using gastric tube. A male baby weighing 3,000 g, with suspicion of EA, was born at gestational age of 37+6 weeks. Gastrostomy was made at an age of two days; seven months later, definite operation was planned. We determined to perform the gastric tube replacement due to long gap revealed by fluoroscopy. Gastric mobilization, gastric tube formation, and pyloroplasty were performed laparoscopically. An isoperistaltic 9 cm gastric tube was made using 2 Endo GIA 45, and interrupted end-to-end esophago-esophagostomy was performed thoracoscopically. With laparoscopy, gastropexy to the diaphragm was performed through the interrupted suture. Operation time was 370 minutes; there was no intraoperative event. Postoperative course was uneventful. He underwent esophageal balloon dilatation due to anastomosis stenosis in the months after surgery.
Single-port laparoscopy-assisted surgery is being performed for various operations in pediatric patients recently. The aims of this study were to prove the safety and find well-matched indications of small bowel resection using single-site umbilical laparoscopic surgery (SSULS).
From 2011 to 2016, 29 pediatric patients underwent SSULS. Medical records were retrospectively reviewed.
A total of 29 patients were included and 30 SSULS were performed in this study. The mean age at operation was 5.7 years, and the mean weight was 21.9 kg. Meckel's diverticulum was the most common indication for SSULS, followed by small bowel intussusception due to leading point mass, small bowel duplication, and Crohn's disease. In most cases, estimated blood loss was negligible except in Crohn's disease with severe inflammation. While answering post-discharge questions about scars, most parents responded that they were satisfied with the postoperative wound.
SSULS is a useful operation to try even for surgeons who do not have advanced laparoscopic skills. Complication rates of single-port operations do not differ from those of conventional laparoscopic operations. Most lesions of the small bowel could be indications of SSULS. Careful attention is required when performing SSULS in patients with Crohn's disease.
Citations

Inguinal hernia in early infant is a challenging surgical condition. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair (LH) for small babies in corrected age 3 months compared with the traditional open inguinal hernia repair (OH).
Medical records were retrospectively reviewed in 232 pediatric patients under corrected age 3 months who underwent inguinal hernia repair from January 1, 2013 to December 31, 2015. The chi-squared and Fisher's exact test were used to analyze the results of the study.
As for operative time, in unilateral/bilateral inguinal hernia repair, OH is faster than LH (p<0.05 vs. p=0.06). But operation time gap is shorter in bilateral hernia than unilateral hernia. As for operation site, bilateral inguinal hernia case was more performed in LH than OH (p<0.05). For comparison with the spontaneous breathing recovery time, there was no statistical difference between the two techniques (p=0.96). As for the recurrence rate, no significant difference was observed between the two techniques (p=0.36), whereas the relative risk of recurrence was higher for OH compared with LH (OR=1.56).
LH is also feasible and safe procedure as OH for small babies in corrected age 3 months for experienced pediatric surgeons.
Citations

This study aimed to assess the long-term clinical outcome of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication (LNF) in children according to their neurologic status.
The study retrospectively analyzed the data of 82 children (62 neurologically impaired and 20 neurologically normal children with primary gastroesophageal reflux disease) who had undergone LNF between 2003 and 2012. The main outcome measures were the occurrence of recurrence that required reoperation and post-procedure complications such as infections, pneumonia, and gastrointestinal complications including ileus, dysphagia, and delayed gastric emptying.
The median age at the time of the LNF was 25 months (range, 1-192 months), and the median of body weight was 10.0 kg (range, 2.8-37.0 kg). The average weight gain was 1.55±1.68 kg at 6 months, 3.32±2.30 kg at 1 year, and 5.63±4.22 kg at 2 years after surgery. Six (9.7%) of the 62 neurologically impaired patients and two (10.0%) of neurologically normal lost their body weight or had no weight changes. Eight (12.9%) of the 62 neurologically impaired children had required redo surgery because of gastroesophageal reflux disease recurrences, while 2 (10.0%) of the 20 neurologically normal children had experienced recurrences. In the neurologically impaired children, the postoperative complications included pneumonia (n=1), wound infection (n=1), urinary tract infection (n=1), dysphagia (n=1), delayed gastric emptying (n=1), and ileus (n=2). All of these complications were not found in the neurologically normal group, except for only one case of infectious colitis. However, there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in postoperative complications.
The outcomes of laparoscopic fundoplication were similar in the neurologically impaired children and in the neurologically normal children.
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) is known to be one of the most common cause of surgery for infants and pyloromyotomy was considered to the standard treatment. There has been an ongoing debate about whether laparoscopic pyloromyotomy (LP) or open pyloromyotomy (OP) is the best option for treating HPS. The aim of this study is to evaluate safety and effectiveness of LP by comparing the clinical results of both surgical strategies performed by single surgeon.
Between January 2000 and December 2013, 60 patients who underwent pyloromyotomy at Asan Medical Center performed by a surgeon were followed: open-supraumbilical incision (n=36) and LP (n=24). The parameters included sex, age and body weight at operation. Clinical outcomes included operation time, time to full feeding, postoperative hospital stay, and postoperative complications.
There were no significant differences in characteristics, postoperative hospital stay between the two groups. Time to full feeding was shorter in LP (OP 24.5 hours vs. LP 19.8 hours; p=0.063). In contrast, the mean operation time was longer in LP (OP 37.5 minutes vs. LP 43.5 minutes; p=0.072). Complications such as perforation of mucosal layer (OP 1 vs. LP 0) and wound problems (OP 2 vs. LP 0) were found to be not worse in laparoscopic group as compared with open group.
There has no difference both laparoscopic and open-supraumbilical incision in terms of postoperative hospital stay, time to full feeds and frequency of complications.
Citations

Laparoscopic appendectomy (LA) has become a gold standard for children even in complicated appendicitis. The purpose of this study was to compare the postoperative surgical site infection rates between laparoscopic and open appendectomy (OA) group in pediatric complicated appendicitis.
A total of 1,158 pediatric patients (age ≤15 years) underwent operation for appendicitis over a period of 8 years. Among these patients, 274 patients (23.7%) were diagnosed with complicated appendicitis by radiologic, operative and pathologic findings, and their clinical outcomes were retrospectively analyzed.
Of the 274 patients with complicated appendicitis, 108 patients underwent LA and 166 patients underwent OA. Patients in the LA group returned to oral intake earlier (1.9 days vs. 2.7 days; p<0.01) and had a shorter hospital stay (5.0 days vs. 6.3 days; p<0.01). However, rate of postoperative intra-abdominal infection (organ/space surgical site infection) was higher in the LA group (LA 15/108 [13.9%] vs. OA 12/166 [7.2%]; p<0.01). Readmission rate was also higher in the LA group (LA 9/108 [8.3%] vs. OA 3/166 [1.8%]; p<0.01).
The minimally invasive laparoscopic technique has more advantages compared to the open procedure in terms of hospital stay and early recovery. However, intra-abdominal infection and readmission rates were higher in the laparoscopy group. Further studies should be performed to evaluate high rate of organ/space surgical infection rate of laparoscopic procedure in pediatric complicated appendicitis.
Citations

Laparoscopic hernia repair in children is still controversial. The aim of this study was to report our long-term results of the laparoscopic hernia technique, which is based on the same surgical principles as conventional open herniotomy.
Five hundred fourteen pediatric patients with inguinal hernia were included in this study under informed consent. All patients underwent a laparoscopic technique of sac transection and intracorporeal ligation. The asymptomatic contralateral inguinal ring was routinely explored and repaired if a patient had patent processus vaginalis on the contralateral side. Patients were prospectively followed for 5 years. Those who were lost to follow-up were excluded from the study. Perioperative complications and recurrences were evaluated.
The mean follow-up period was 29 months. Mean operation time was 27.5 minutes. Forty one percent of the patients had contralateral patent processus vaginalis. Only one hernia recurred (0.19%). We had one case of contralateral metachronous hernia (0.21%) during follow-up period.
The long-term follow-up results of our study revealed that laparoscopic hernia sac transection and ligation can be a safe and effective alternative for conventional herniorraphy.
Citations

Laparoscopic surgery has become popular in the past few decades, owing to less postoperative pain, fast recovery, and better cosmetic outcomes. The laparoscopic approach has been employed in pediatric surgery for the same reasons. After the first attempts of single incision laparoscopic appendectomy in pediatrics in 1998, single incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS) has recently been proven to be safe and feasible for the pediatric population. However, limitations have been reported for SILS, such as the wide learning curve, compared to standard laparoscopic surgery, and the restricted number of hospitals with surgical training programs including SILS. In this study, we intend to present our initial experiences with SILS in children, and to describe the technique, instruments used, and outcomes. This is a retrospective study of 71 pediatric patients who underwent SILS, at a tertiary medical center, between September, 2012 and August, 2013. Electronic medical records were reviewed for demographics, type of procedure, operation time, use of additional ports, conversion to open surgery, complications and hospital stay. Additional ports were inserted in 4 cases, for the purpose of traction. Postoperative complications were noted in 13 cases, which were mostly related to wound inflammation or formation of granulation tissue. According to our analyses, patients with complications had significantly longer use and more frequent use of pain killers. Notwithstanding the small sample size, many of the procedures performed in pediatric patients seem to be possible with SILS.
Citations

Intussusception is common cause of intestinal obstruction in children. Most of intussusceptions can be treated with non-operative reduction using air or barium. However, about 10% patients need operative treatment due to failure of reduction, peritonitis, and recurrence after reduction. We introduce our experience of laparoscopic surgery for intussusception. From April 2010 to March 2013, we reviewed 57 children who diagnosed intussusception. Twelve patients underwent an operation. The cause of operation was 7 of failure of air reduction and 5 of recurrence after air reduction. Median age was 21.5 months (range: 5.0~57.7 months) and 11 children (91.7%) underwent successful laparoscopic reduction. Median operating time was 50 minutes (range: 30~20 minutes) and median hospital days was 4.5 days (range: 3~8 days). One patient had a leading point as a heterotopic pancreas and underwent bowel resection through conversion. There was neither intra-operative nor postoperative complication. Laparoscopic reduction for intussusception can bring an excellent cosmetic effect with high success rate.
The purpose of this study is to analyze the early experience of the laparoscopic adhesiolysis for the intestinal obstruction due to postoperative adhesion. Seven patients were included in this study. The median age of those patients was 13, and there were 3 males and 4 females. Previous diagnosis and surgical procedure were various in seven cases, including small bowel resection with tapering enteroplasty, Boix-Ochoa fundopl ication, Ladd's procedure with appendectomy, mesenteric tumor resection with small bowel anastomosis, ileocecal resection and anastomosis, primary gastric repair, and both high ligation. A successful laparoscopic adhesiolysis was performed in one who had high ligation for inguinal hernia and had a single band adhesion. Six out of 7 (86%) cases needed to convert open surgery due to multiple and dense type of adhesion. In conclusion, laparoscopic approach with postoperative small bowel adhesion seems safe. However, it might be prudently considered because of high rates of conversion in children.
Although hemangiomas are common vascular tumors that can occurany where in the body, they seldom involve the gastrointestinal tract. Hemangiomas of the gastrointestinal tract in infants and children are rare benign vascular tumors that most commonly present with gastrointestinal bleeding. We describe here the case of 2-year-old boy with intestinal bleeding caused by a large jejunal cavernous hemangioma, which was treated by laparoscopy-assisted resection of the affected portion of the jejunum.
Minimally invasive techniques for pediatric inguinal hernia repair have been evolving in recent years. We applied the laparoscopic method to repair pediatric inguinal hernia using the techniques of sac transection and intra-corporeal ligation. Between November 2008 and August 2010, 67 pediatric patients (47 boys and 20 girls) with inguinal hernias were included in this study. Postoperative activities, pain, and complication were checked prospectively at regular follow-up. One patient presented with clinically bilateral hernia, and three patients had metachronous hernias. Thirty-two cases out of 63 patients with unilateral hernias had a patent processus vaginalis on the contralateral side. Mean operation time was 35±11.4 minutes for unilateral hernias and 43±11 minutes for bilateral hernias. There were no intra-operative complications. One patient had a small hematoma on the groin postoperatively, which subsided spontaneously in a week. Recurrence and metachronous hernia were not found at follow up. In summary, laparoscopic inguinal repair in children is safe, easy to perform and has an additional advantage of contralateral exploration. Further studies should include long term follow-up.
Citations

There have been no definitive preoperative diagnostic imaging studies for impalpable testes. We observed the effectiveness of laparoscopy for detecting impalpable testes not identified with ultrasonography (USG) or careful physical examination under general anesthesia. We retrospectively reviewed 117 patients (118 testes) who were operated upon for undescended testes from January 1998 to December 2004. The testes of these patients were palpable in 97(82 %) and impalpable in 21 (18 %). We analyzed the preoperative diagnostic method, site of the testes, operative method and operative findings of the 21 impalpable testes. Preoperative USG and physical examination under general anesthesia were performed on 20 patients, and 12 patients' testes could be localized. Eight patients whose testes could not be localized with USG and physical examination underwent laparoscopy. Seven of the 8 patients had testes in inguinal canal and 4 of these were atrophied and underwent orchiectomy because of atrophy (2) and vanishing (2). Only 1 patient had bilateral intraabdominal testes and one of the testes was atrophied. Laparoscopy was a useful method for detecting impalpable testes, but the clinical application might be limited because the location of atrophic or vanishing testes was mainly inferior to internal inguinal ring.
Pediatric laparoscopic appendectomy is controversial particularly in complicated appendicitis. We evaluated the outcomes of laparoscopic appendectomy (LA) and open appendectomy (OA) in simple appendicitis and complicated appendicitis respectively. Since June 2004, initial LA has been our policy in all appendicitis including complicated ones. A total of 160 patients were included in this study, consisting of 80 OA (August 2001 . August 2003) and 80 LA (June 2004 . June 2006). We compared the operating time, the length of hospital stay, the length of antibiotics use, and the postoperative complications between LA and OA. In simple appendicitis (73), there were no differences between LA and OA. However in the 87 patients with complicated appendicitis, the operating time was longer in LA (64.8 min vs. 50.2 min) but the length of hospital stay was shorter in LA than OA (8.5 days vs. 9.6 days). There was one complication in simple appendicitis group and six in complicated appendicitis group (3 cases in LA, 3 cases in OA). There was no difference in the results of LA versus OA in simple appendicitis. Therefore for simple appendicitis, LA is recommended in consideration of the cosmetic effect (fewer scar). In complicated appendicitis, early discharge was an advantage and there were no differences in complications in LA despite a longer operative time. So we conclude LA can be considered as the first choice of treatment for all pediatric appendicitis including complicated appendicitis. To confirm our impressions, more well controlled randomized prospective studied need to be done.
Citations

Appendicitis is the most common surgical emergency in childhood and the technologic advances of modern medicine have affected the diagnosis and treatment of appendicitis. This study is to evaluate the differences in diagnosis and treatment of appendicitis between present and 10 year ago. The authors retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients who underwent appendectomy under the diagnosis of the acute appendicitis from July 1993 to June 1995 (Group A, n = 78) and from July 200 to June 2005 (Group B, n = 105). There are no differences between group A and B in mean age (8.5 ±3.6 vs. 9.3 ±3.1 year), duration of symptoms (3.0 ±3.2 vs. 2.6 ±3.8 days), and postoperative hospital stay(6.6 ±4.8 vs. 5.8 ±3.6 days). Preoperative abdominal ultrasonogram and/or computed tomogram was performed in 7 patients (9.0 %) of group A and in 51 patients (58.5 %) of group B. Thirty-six patients (34.3 %) of group B underwent laparoscopic appendectomy, but none in group A. Incidence of a histologically normal appendix decreased from 15.8 % in group A to 4.8 % in group B (p =0.018). This study suggests that utilization of abdominal ultrasonogram or computed tomogram in preoperative evaluation become more popular and surgical treatment of acute appendicitis become more minimally invasive. The rate of negative appendectomy was also reduced compared with 10 year ago.
Citations

Fundoplication is accepted as an effective treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. The recent results of laparoscopic fundoplication demonstrated safety and less morbidity, shorter hospital stay and less pulmonary complication compared to the open operation. Laparoscopic fundoplication has been our first choice of operation for gastroesophageal reflux disease since 2003. Among 29 cases, there were 2 conversion cases because of severe distension of transverse colon and hepatomegaly. We studied 27 consecutive patients operated upon from January 2003 through December 2004. There were 15 boys and 12 girls, ages from 1.5 months to 12 years (median 25.3 months). Body weight ranged from 2.9 kg to 37 kg (median 9.8 kg). Neurological abnormalities were present in 23 patients. Indications for surgery included medically refractory reflux associated with vomiting, pneumopathy, otorhinolaryngologic pathology, failure to thrive, esophagitis, apnea and bradycardia. We used 4-5 trocars of 5 mm or 12 mm with 30° telescope and performed the Nissen technique in all patients. In neurological impaired patients, gastrostomy tube was placed at the time of fundoplication. Median operative time was 130 minutes (70 - 300 minutes). There was no mortality nor intraoperative complication. Twenty-six patients were followed for median of 19 months (8 - 31 months). Four patients (15.4 %), who were all neurological impaired, developed recurrent symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Two of these patients had reoperation (1 laparoscopic approach, 1 open method). There were significant increases in body weight in 11 patients after fundoplication. Laparoscopic fundoplication is acceptable as a safe and effective method for gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Citations

The laparoscopic splenectomy (LS) became popular over the last 10 years. The advantage of LS over open splenectomy (OS) includes short hospital stay, improved cosmesis, less development of postoperative intestinal ileus, and less analgesics required. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the outcome of LS at Asan Medical Center from January 1999 to January 2003. The records of 14 consequent children who underwent splenectomy were reviewed retrospectively. Patients characteristics, morbidity, mortality, operative time, blood loss, and hospital stay were analyzed., Seven patients age 5 to 15 years underwent LS under the indications: idiopathic thrombocytic purpura (ITP, n=3), hereditary spherocytosis (n=3), and myelodysplastic syndrome (n=1). Seven patients, age 7 to 16 years, underwent OS during the same period for ITP (n=7). Median operative time was 120 minutes (80 to 170 mins.) in OS, and 270 minutes (110 to 480 mins.) in LS (p<0.05). Median length of hospital stay was 6 days (3 to 8) in OS, and 4 days (3 to 6) in LS (p>0.05). Median splenic length was 12.0 cm (9.2 to 18.0) in OS, 14.0 cm (10.0 to 19.5) (p>0.05). Accessory spleens were identified in 3 of 7 LS and 1 of 7 OS cases. In the LS group, there was no conversion to open surgery. Two patients in LS required blood transfusion postoperatively. LS in children can be performed as effectively and safely as OS.
Appendicitis is the most common surgical emergency in childhood. Open techniques have been adopted in children after experiences in various surgical conditions in adults has accumulated. It is debatable whether Laparoscopic appendectomy (LA) is superior to open appendectomy (OA) in children. The goal of this study is to review the results of laparoscopy and laparotomy in the nonperforated appendicitis. The records of 22 patients under 15 years of age who were operated upon for nonperforated appendicitis at Asan Medical Center were analyzed between December 2002 and April 2003. Age, type and length of intervention, frequency of analgesic use, complication, length of hospitalization, and cost for each treatment groups (N=11) were compared. Laparoscopy patients were older (13.0 vs. 10.1 years; p > 0.05), and operative time was longer (55.0 vs. 35.0 minutes; p < 0.05). There was no conversion (OA to LA). The median length of hospital stay was significantly shorter in laparoscopy (3.0 vs. 2.0 days; p < 0.05). The median cost for LA was more expensive (W833, 836 vs. W751,398; p < 0.05). Even though there were higher costs and longer operative times with laparoscopic procedures, the shorter hospital stay was an advantage.
Citations

When jaundice persists for more than 14 days postnatally, the early diagnosis of surgical jaundice is important for the prognosis in extrahepatic biliary atresia after draining procedure. The role of diagnostic laparoscopy to differenctiate medical causes of jaundice from biliary atresia is evaluated in this report. Four patients with prolonged jaundice have been included in this study. When the gallbladder was not visualized we proceeded to laparotomy. In patients with enlarged gallbladder visualized at laparoscopy, laparoscopic guided cholangiogram was performed, and laparoscopic liver biopsy was done for those who had a patent biliary tree. Two patients had small atretic gallbladder and underwent a Kasai hepato-portoenterostomy. One patients showed a patent gallbladder and common bile duct with atresia of the common hepatic and intrahepatic ducts, and they underwent a Kasai hepatic-portoenterostomy. One patient showed an enlarged gallbladder and laparoscopic-guided cholangiogram were normal. Laparoscopic liver biopsy was performed. There were no complications. Laparoscopy wth laparoscopic-guided cholangiogram may be a valuable method in accurate and earlier diagnosis in an infant with prolonged jaundice.
We analyzed our experience of orchidopexies performed during last 10 years to evaluate results and to determine the possible approach to the treatment of undescended testes. Between 1988 and 1997, we had treated 420 undescended testes (314 palpable and 106 nonpalpable) in 356 boys. Average patient age at presentation was 4.1 years with 40.2% presenting before the age of 2 years. Of 106 nonpalpable testes, 23 testes were intraabdominal, 32 were preperitoneal and 51 were absent at the surgery. During the period of first 5 years, we had performed the surgery through 31 inguinal and 13 midline transabdominal incisions for 44 patients nonpalpable testes, while during the later 5 years, all 47 patients nonpalpable were treated through inguinal incisions. For the nonpalpable testes, the inguinal approach with or without intraperitoneal extension was successful in defining the location of testes and blind-ending vessels in all patients. Laparoscopy was not helpful in avoiding surgical exploration in all our patients with nonpalpable testes. Of 339 inguinal and midline transabdominal orchidopexies without spermatic vessels ligations, 324 testes were placed in the scrotum, 4 in the upper scrotum and 3 in the inguinal area. Eight were resulted in atrophy. Of 13 Fowler-Stephens orchidopexies, 7 were placed in the scrotum and 6 were resulted in atrophy. Testicular growths were noticed in most patients who underwent orchidopexies and the volume of fixed testes became as large as the contralateral normal testes by the mean duration of 43.3 months postoperatively. In conclusion, orchidopexies were successful in most cases of cryptorchidism in terms of testicular position and growth. However, there were more testicular atrophies in patient in whom spermatic vessels were ligated. In cases of nonpalpable undescended testis, the inguinal approach with or without intraperitoneal extension would be recommended.

