Lymphatic malformations (LMs) are congenital malformations of the lymphatic system which can be effectively treated by sclerotherapy. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of doxycycline in the treatment of LMs.
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of all patients who were diagnosed as LMs and underwent doxycycline sclerotherapy in Asan Medical Center between March 2013 and February 2014. Thirty-five sclerotherapy procedures were performed on 21 patients. The procedures were performed under general anesthesia. After each treatment, the clinical and radiographic response was characterized as complete (≥80% decrease in lesion size), partial (<80% decrease of size), or no response (no decrease of size).
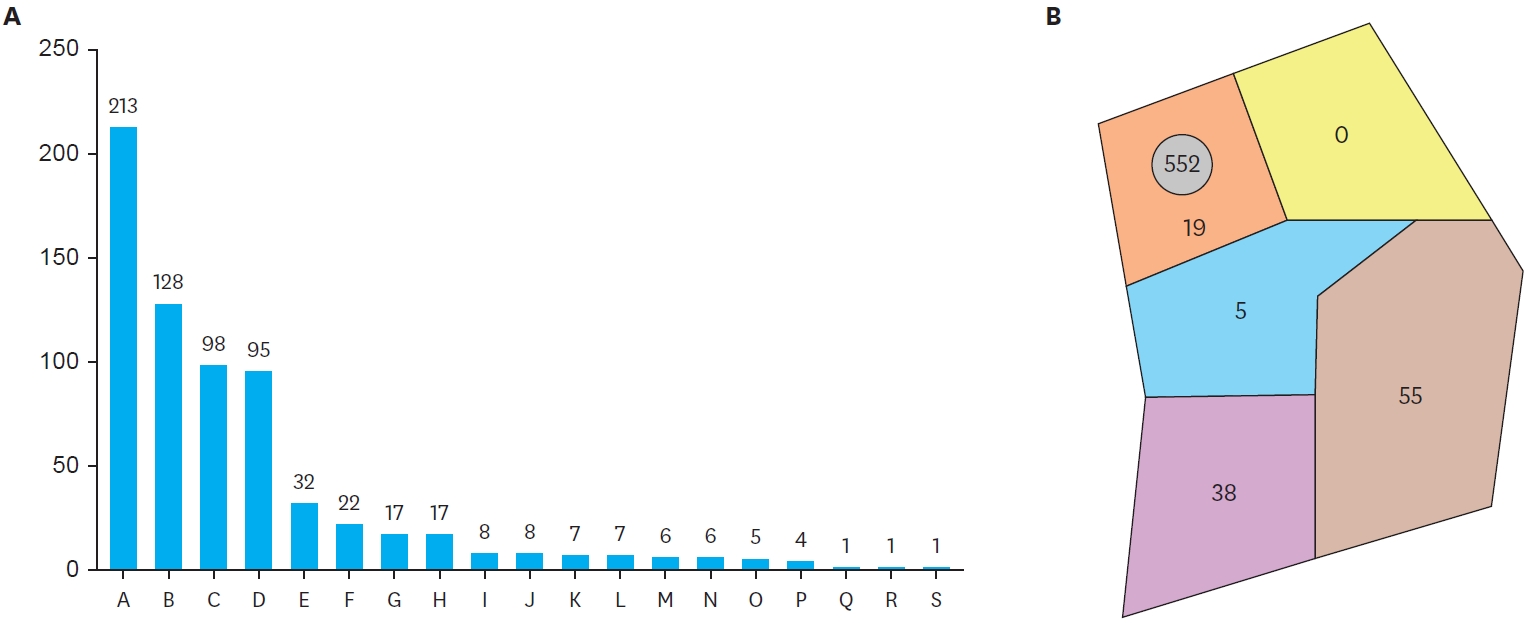
There were 11 male patients and 10 female patients. The median age of sclerotherapy was 21 months (range, 2–180 months). The most common location was cervicofacial (52.3%), followed by extremity (28.6%) and truncal (19.0%). The most common lesion type was macrocystic (71.4%), followed by microcystic (28.5%). There was one (2.8%) skin necrosis which was recovered by wound management. Thirty-eight percent of patients had a complete response, 47.6% of patients had a partial response and 14.3% of patients had no response. Median frequency of treatment was one (range, 1–5). No response group consisted of all microcystic type.
Sclerotherapy with Doxycycline is safe and effective for macrocystic LMs.
Citations

We evaluated perioperative and long-term outcomes of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) and established indications of MIS in solid pseudopapillary tumor (SPT) in pediatric patients.
From October 1992 to April 2018, 66 patients (age, <18 years) diagnosed with SPT underwent either open pancreatectomy (OP) or MIS. Variables including postoperative complications and recurrence rates were retrospectively analyzed.
Thirty-five patients underwent open surgery and 31 underwent laparoscopic/robotic surgery. Mean tumor size in MIS was significantly smaller than that in OP (4.3±1.8 cm vs. 7.6±3.5 cm, p=0.005). There were 4 cases of open conversion from laparoscopic surgery because of vessel encasements (n=2), bleeding (n=1), and pancreatic ductal injury (n=1). Solitary pseudopapillary carcinoma was diagnosed in 6 patients. Recurrence was observed in 3 and 1 patients who underwent OP and MIS, respectively (p=0.634). Tumor size, mass size/abdominal diameter (MS/AD) ratio, and degree of the portal or superior mesenteric vein involvement were the most important indications for MIS.
MIS is being widely used in pediatric surgeries with increased expertise and safety, especially in pancreatic diseases. Careful patient selection for MIS in regards with parameters such as MS/AD ratio and vessel abutment might be a feasible choice.
Citations

Barium enema is one of the diagnostic modalities for Hirschsprung'sdisease. The present study aimed to investigate the diagnostic accuracy of barium enema for Hirschsprung's disease, especially total colonic aganglionosis (TCA).
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of all the patients who were diagnosed as having TCA and underwent a barium enema in Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital between January 1998 and December 2016. All the tests were performed and reviewed by pediatric radiologists.
Among the total 19 patients with TCA who underwent barium enema, 9 patients (47.4%) had accurate radiographic results. Eight of the 13 neonate patients (61.5%) showed typical TCA radiological findings. However, only one of the 6 patients aged >4 weeks (16.7%) had accurate radiological diagnosis.
Barium enema showed low accuracy for TCA, and its diagnostic performance was better in neonatal period than in those aged >4 weeks.
Recent data suggest that monotherapy with a broad-spectrum antibiotic may be as efficacious as, and potentially less costly than, standard multi-drug therapy. We compared mono-therapy with intravenous piperacillin-tazobactam (PT) with multi-drug therapy with cefotaxime and metronidazole (CM) in aspect of postoperative complications and hospital stay.
We reviewed the hospital records and medical costs of the pediatric patients who were managed for perforated appendicitis between April 2013 and May 2014 retrospectively.
Forty-six patients with laparoscopic appendectomy for perforated appendicitis were included in our study. PT group was 20 and CM group was 26 patients. On admission, there were no significance in sex distribution, duration of symptoms, leukocyte count, and CRP levels. At postoperative third, fifth, and seventh day of each regimen, PT group have no statistical difference with CM group in leukocyte count, percentage of neutrophil, and CRP. There was no difference in abscess formation rate, wound infections, and hospital stay between two groups. There was only one patient who was readmitted with elevation of CRP and leukocyte count in CM group.
Daily dosing with the mono-therapy of PT offers as efficient as multi-drug therapy of CM. To evaluate the efficacy of broad-spectrum antibiotics monotherapy in perforated appendicitis children, the cohort included more patients should be needed.
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) is known to be one of the most common cause of surgery for infants and pyloromyotomy was considered to the standard treatment. There has been an ongoing debate about whether laparoscopic pyloromyotomy (LP) or open pyloromyotomy (OP) is the best option for treating HPS. The aim of this study is to evaluate safety and effectiveness of LP by comparing the clinical results of both surgical strategies performed by single surgeon.
Between January 2000 and December 2013, 60 patients who underwent pyloromyotomy at Asan Medical Center performed by a surgeon were followed: open-supraumbilical incision (n=36) and LP (n=24). The parameters included sex, age and body weight at operation. Clinical outcomes included operation time, time to full feeding, postoperative hospital stay, and postoperative complications.
There were no significant differences in characteristics, postoperative hospital stay between the two groups. Time to full feeding was shorter in LP (OP 24.5 hours vs. LP 19.8 hours; p=0.063). In contrast, the mean operation time was longer in LP (OP 37.5 minutes vs. LP 43.5 minutes; p=0.072). Complications such as perforation of mucosal layer (OP 1 vs. LP 0) and wound problems (OP 2 vs. LP 0) were found to be not worse in laparoscopic group as compared with open group.
There has no difference both laparoscopic and open-supraumbilical incision in terms of postoperative hospital stay, time to full feeds and frequency of complications.
Citations

Gastroschisis and omphalocele are major anterior abdominal wall defects. The purpose of this study was to analyze the clinical differences and mortalities of gastroschisis and omphalocele in Asan Medical Center.
A retrospective review of the medical records was conducted of 103 cases of gastroschisis and omphalocele from September 1989 to February 2013 in Asan Medical Center in Korea.
There were 43 cases (41.7%) of gastroschisis and 60 cases (58.3%) of omphalocele. There was a female predominance in both gastroschisis (60.5%) and omphalocele (58.3%). The average gestational age at delivery was 36.7±0.4 weeks for both groups. The mean birth weights were 2,381.9±80.6 g for gastroschisis and 2,779.4±82.8 g for omphalocele (p=0.001). Mean maternal ages in the gastroschisis and omphalocele groups were 27.5±0.7 years and 30.5±0.7 years, respectively (p=0.002). Associated malformations were documented in 13 infants (30.2±) with gastroschisis and 46 infants (76.7±) with omphalocele (p<0.001). All of gastroschisis patients except one underwent surgery including 31 primary repairs and 11 staged repairs. Fifty-two infants with omphalocele underwent surgery-primary repair in 41 infants and staged repair in 11 infants. Among 103 cases, 19 cases (18.4%) expired. Mortality rates of gastroschisis and omphalocele were 23.3% (10/43 cases) and 15.0% (9/60 cases), respectively (p=0.287). The main causes of death were abdominal compartment syndrome (6/10 cases) in gastroschisis, respiratory failure (4/9 cases) and discharge against medical advice (4/9 cases) in omphalocele.
Gastroschisisis was associated with younger maternal age and lower birth weight than omphalocele. Associated malformations were more common in omphalocele. The mortality rates did not make a statistical significance. This might be the improvement of treatment of cardiac anomalies, because no patient died from cardiac dysfunction in our study. Furthermore, abdominal compartment syndrome might be the main cause of death in gastroschisis.
Citations

The purpose of this study was to compare the diagnostic accuracy of the non-invasive diagnostic methods and rectal suction biopsy for the detection of Hirschsprung disease (HD).
We reviewed diagnostic methods and results retrospectively in patients who underwent anorectal manometry, barium enema and rectal suction biopsy for the diagnosis of HD at Asan Medical Center from January 2000 to December 2012.
There were 97 patients (59 neonates and 38 infants) in the study period. The overall accuracy of anorectal manometry for the diagnosis of HD was 71.1% and its sensitivity was 51.4% (48.1% in neonate and 62.5% in infant, respectively) and its overall specificity was 82.3% (81.3% in neonate and 83.3% in infant, respectively). The Overall accuracy of barium enema was 66.0% (72.8% in neonate and 55.3% in infant, respectively) and specificity of barium enema was 53.2% (56.3% in neonate and 50.0% in infant, respectively). These results were lower than those of anorectal manometry. The overall sensitivity of barium enema was 88.6% (92.6% in neonate and 75.0% in infant, respectively) and it was higher than the sensitivity of anorectal manometry. Histological studies confirmed HD in 35 patients, in one of whom the suction biopsy showed negative finding.
Accuracy of non-invasive methods for diagnosis of HD in our study is lower than those in previous study, so we need to improve the quality of diagnostic tools in our hospital. We conclude that the rectal suction biopsy is the most accurate test for diagnosing HD, so the biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of the HD is very important.
Citations


