Total proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (T-IPAA) in childhood is a surgical procedure mainly applied to familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or ulcerative colitis (UC), but it can be applied to non-FAP/non-UC disease (NFNU). Studies regarding the role of T-IPAA who underwent the operation in childhood, especially in terms of long-term gastrointestinal function, complications, and quality of life (QOL) are limited. The aim of this study was to evaluate the characteristics of patients receiving T-IPAA and to compare their bowel function outcomes and QOL.
Patients aged ≤18 years at the time of T-IPAA were included. Their medical records were retrospectively reviewed. Krickenbeck classification, Cleveland Clinic Incontinence (CCI) score, 36-item Short-form Health Survey Questionnaire, and Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index were used for the evaluation of bowel function and QOL. The median follow-up period was 9.8 years.
Of the 25 patients, 9 had FAP, 9 had UC, and 7 had NFNU. NFNU include 3 of Hirschsprung disease, 2 of intestinal neuronal dysplasia, and 2 of imperforate anus. The median age at T-IPAA was 17.8, 14.2, and 9.3 years for FAP, UC, and NFNU, respectively (p=0.001). Bowel function was satisfactory in terms of voluntary bowel movement (VBM), soiling, and constipation. VBM and constipation were not different between the groups, but soiling was most in NFNU (100%, p=0.047). However, QOL was best in the NFNU group in surveys (p=0.034 and 0.004, respectively).
T-IPAA could be safely applied not only for FAP and UC but also for other diseases in selective cases, with caution.
Citations

Preoperative ultrasonography (USG) in pediatric inguinal hernia has controversy. In this study, we analyzed the cases of pediatric inguinal hernia with/without preoperative USG and discussed whether USG is necessary.
We reviewed medical records of 1,441 patients who underwent inguinal hernia repair in Seoul National University Children's Hospital between January 2011 and August 2016 retrospectively.
Male were 69.3% and age at operation was 37.8±36.5 months old. There were 150 patients (10.4%) performed USG preoperatively. The department ordered to perform USG included department of surgery (n=71), emergency medicine (n=42), pediatrics (n=26), urology (n=10) and outside hospital (n=1). The reasons of performing USG included evaluation for hernia laterality (n=82), incarceration (n=28), testis (n=15), request of parents (n=14), scrotal mass (n=6) and incidentally found during evaluation for another disease (n=5). Excepting 5 cases of incidental finding, of 145 cases with USG, 12 (8.3%) cases changed the surgical plan; change to bilateral repair from unilateral repair (n=5), emergency operation due to incarceration (n=4) which include 1 salpingo-oophorectomy, 1 open abdomen surgery and 2 hernia repair after reduction of ovary, change to co-operation of orchiopexy (n=2) and change to laparoscopic surgery from open surgery due to herniation of both ovaries into one inguinal canal (n=1). In group without USG (n=1,291), 5 patients (0.4%) had unexpected problems during operation; 2 co-operation of orchiopexy because of transverse testicular ectopia (n=1) and right undescended testis (n=1), 2 hypertrophy of major labia and 1 retroperitoneal lymphangioma at inguinal area misdiagnosed as inguinal hernia.
It was difficult to interpret the meaning of preoperative USG because not all patients had performed it. In this study, 10.4% of patients performed USG and 8.3% of them changed surgical plan. About 0.4% of patients without preoperative USG would have benefited from it for surgery if they had performed it. Since the percentage is too low, it is unreasonable to conclude that USG has diagnostic utility in inguinal hernia in this study.
An 18-year-old male patient with cerebral palsy and scoliokyphosis came to the emergency department with abdominal distension and vomiting. He was a situs inversus patient with a feeding gastrostomy tube. Sigmoid volvulus was initially suspected, so rectal tube insertion and endoscopic decompression were attempted, but failed. So he went through explorative laparotomy, and transverse colonic adhesion and twisting around the gastrostomy tube and gastric wall was identified. Adhesiolysis and resection with redundant transverse colon and end-to-end colocolic anastomosis was performed. He discharged with symptom free. Suspecting transverse colonic volvulus is important when the patient has anatomical anomalies and feeding gastrostomy tube. Timely diagnosis with proper radiologic imaging should be made. Surgical resection of the redundant colon is needed for successful management of transverse colonic volvulus.
Citations

Gardner-associated fibroma (GAF) is a benign lesion of soft tissue which has recently been described and is exceedingly rare in children. GAF is associated with adenomatous polyposis coli gene mutation, familial adenomatous polyposis and desmoid. We report a case of patient with soft tissue tumor on her lower back which was turned out to be GAF. The patient was a 19-month-old female who visited out-patient clinic with palpable mass on her lower back and we performed surgical excision. The tumor was located at subcutaneous and we excised the tumor including surrounding soft tissue. She discharged without any complication on surgery day. The pathologic report showed dense collagenous tissue with spindle cell and adipose tissue, suggestive of GAF. We are planning to check gene study and to perform endoscopy and abdominal ultrasonography for at the age of 4.
Anorectal duplications account for only 5% of gastrointestinal duplications, and cases with involvement of the anal canal are much rarer. Nearly all anorectal duplications are posterior to the rectum; duplications located anterior to the normal rectum are highly unusual, and only a few cases have been reported. We report the case of an anterior anorectocolonic duplication presenting as a rectovaginal fistula in a 2-month-old infant. After diagnosis, the duplication was excised completely without further intestinal complications.
Thyroid cancer is a rare disease in pediatric population, but its incidence rate is increasing. The aim of this report is to present a single institution experience of pediatric thyroid cancer and to identify clinical features, predisposing factors, and postoperative course of pediatric thyroid cancer.
We retrospectively reviewed 35 pediatric patients who underwent operation due to thyroid cancer at Seoul National University Children's Hospital between May 1997 and January 2017. The median follow-up period was 70 months (range, 5–238 months).
The mean age at operation was 12.0±5.91 years and 27 patients were female. The underlying conditions in patients included history of chemoradiotherapy for previous other malignancies (n=4), hypothyroidism (n=3), history of chemotherapy (n=2), family history of thyroid cancer (n=1) and history of radiation therapy (n=1). The initial symptoms were palpable neck mass (n=21) and incidental findings (n=11). Total thyroidectomy (n=30) or unilateral lobectomy (n=5) were performed. There were 15 postoperative complications including transient hypocalcemia in 14 patients and Horner's syndrome in 1 patient. The most common pathologic cell type was papillary thyroid cancer (n=29). Extrathyroid extension and lymph node invasion were found in 25 patients and 27 patients, respectively. Thirteen patients showed multifocality. During follow-up period, 5 patients underwent additional operation because of tumor recurrence in lymph nodes. Lung metastasis was detected in 3 patients at the time of diagnosis and in 3 patients during follow-up period. The mortality rate was zero and mean disease-free survival was 83.7±47.9 months.
Pediatric thyroid cancer has lower mortality rate and recurrence rate as seen in this study despite the advanced stage at diagnosis. A thorough follow-up of patients with an underlying condition such as history of chemoradiotherapy and understanding new pediatric guideline can be helpful to maximize patients' survival and prognosis.
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) in abdomen and thorax has been widely accepted for pediatric diseases. Thoracoscopic surgery has the advantage of less pain, better cosmetic outcomes and less musculoskeletal sequelae in comparison to open surgery. We would like to share our initial experience with thoracoscopic surgery performed by one pediatric surgeon.
We performed a retrospective review of patients who underwent thoracoscopic surgery by one pediatric surgeon between April 2010 and August 2017 in Department of Pediatric Surgery, Seoul National University Children's Hospital.
There were totally 18 cases; 8 cases for esophageal atresia, 3 cases for congenital diaphragm hernia, 2 cases for diaphragm eventration, 2 cases for esophageal duplication cyst, 2 cases for pleural mass and 1 case for esophageal bronchus. At the operation, median age was 9.5 months (range, 0-259 months) and median body weight was 9.4 kg (range, 1.9-49.4 kg). Median operative time was 157.5 minutes (range, 45-335 minutes). There was no case of open conversion and 2 cases of minor leakage at anastomosis site in case of esophageal atresia. Median follow-up month was 5 months (range, 0-87 months). During follow-up, 4 cases of esophageal atresia showed anastomosis site narrowing and average 2.5 times (range, 1-5 times) of esophageal balloon dilatation was done.
We performed thoracoscopic surgery in case of esophageal, diaphragm disease and pleural mass. Thoracoscopic surgery can be an effective and feasible option of treatment for well-selected pediatric patients of intra-thoracic disease including esophagus, diaphragm and mediastinum disease.
Soft tissue hemangioendothelioma (STHE) is a rare vascular tumor, which has a similar prognosis to borderline malignancy. The disease is poorly understood in pediatric cases because of its low incidence; therefore, we investigated treatment strategies for STHE in children.
We retrospectively analyzed 8 patients with STHE, who were pathologically confirmed between January 1995 and June 2015. The median duration of follow-up was 72 months.
Five were male and the median age at the time of surgery was 1.2 years. Six patients presented with a palpable mass, and 2 patients experienced facial paralysis. The median tumor size was 4.0 cm. The following tumor locations were observed head (2 patients), neck (2 patients), chest wall (1 patient), sacrococcyx (1 patient), upper limb (1 patient), and lower limb (1 patient). The patients underwent either microscopic complete resection (R0) (3 patients), macroscopic complete resection (R1) (2 patients), or macroscopic incomplete resection (R2) (3 patients). After histopathological examination, 6 patients were diagnosed with kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (HE), one with retiform HE, and one with epithelioid HE. Postoperative sequelae occurred as gait disturbance, hearing impairment, and vocal cord palsy. Tumor recurrence or regrowth occurred in 4 patients. These patients underwent reoperation and IFN therapy; however, in the patient with epithelioid HE, metastasis to the scalp occurred after these therapies. The patient with the head tumor who underwent R2 resection, underwent resection three more times, but died 11 months after the first surgery.
When treating STHE in children, R0 resection should be first considered, but recurrence and metastasis should be monitored depending on the size, pathology, and location of the lesion. When major sequelae are expected, function-preserving surgery could be considered, depending on tumor location, size, and nearby organs.
Lymph node enlargement is a common finding in children suggesting normal or benign. Palpable nodes which are large, hard or fixed must be examined carefully to rule out malignant diseases. In this case, a 15-year-old boy presented to our hospital to inspect the palpable mass at his post-auricular area being found 2 months ago. It was diagnosed as nodal marginal zone lymphoma (NMZL) through excisional biopsy and immunohistochemistry. NMZL is very rare, especially in children and young adults, but occurs locally in most cases with a good prognosis compared to adults. We described a rare case of NMZL diagnosed in adolescent.
Number of pediatric cholecystectomy has been recently showing a gradually increasing trend. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical features of patients who underwent pediatric cholecystectomy, and the latest trend in cholecystectomy.
In the present study, we conducted a retrospective chart review on 47 patients who had undergone cholecystectomy at a single center. The entire patient population was divided into two groups, according to the time of cholecystectomy (early group, January 1999 to December 2006; late group, January 2007 to August 2014).
The comparison between the early and late groups showed that the number of cholecystectomy increased from 13 to 34 cases representing a 2.6-fold increase. The mean patient age also increased from 5.94±4.08 years to 10.51±5.57 years (p=0.01). Meanwhile, laparoscopic surgery also increased from 15.4% to 79.4%, respectively (p<0.001). However, sex, mean body mass index, comorbidities, indications of cholecystectomy, and previous total parenteral nutrition were not statistically significant.
The results of this study showed that pediatric cholecystectomy cases are increasing, particularly in the 10 to 19 years age group and laparoscopic cholecystectomies are also being performed at an increasing rate. When the patients were compared according to the time of cholecystectomy, there were no differences in other risk factors or indications for cholecystectomy.
Citations

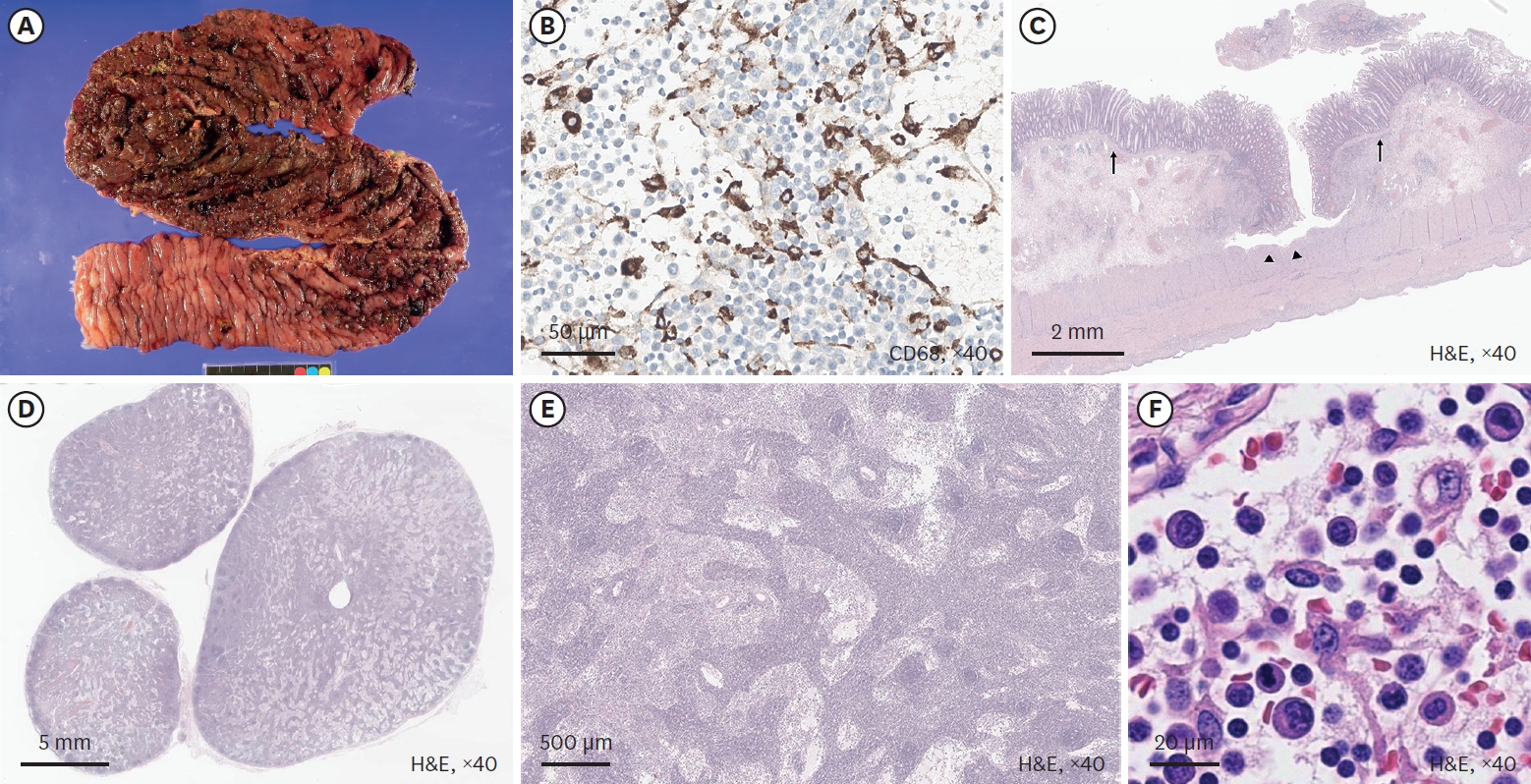
Mixed acinar-neuroendocrine carcinoma (MANEC) is a malignant pancreatic tumor that rarely occurs in children. It is diagnosed pathologically according to the proportion of neuroendocrine cells present, highlighting the need for surgical biopsy. A 13-year-old boy presented with a 10-cm palpable mass on CT. Surgical resection was performed, and the pathological diagnosis was MANEC. There were no postoperative complications, and the patient was discharged from the hospital 10 days after surgery. He is presently undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy. We reviewed historical MANEC cases published in the English literature. We concluded that pathological analysis of a surgically resected specimen is necessary for an accurate diagnosis of MANEC, and that publication of more cases is needed to determine the optimal management strategy for MANEC.
Citations


