Division of Pediatric Surgery, Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Copyright © 2012 Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons
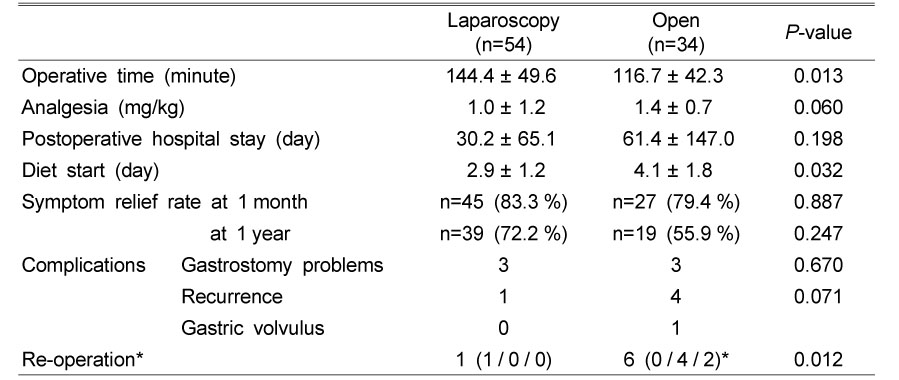
(P-value: Fisher's Exact Test)
*Cause of Re-operation (Gastrostomy problem/Recurrence/Other problems)
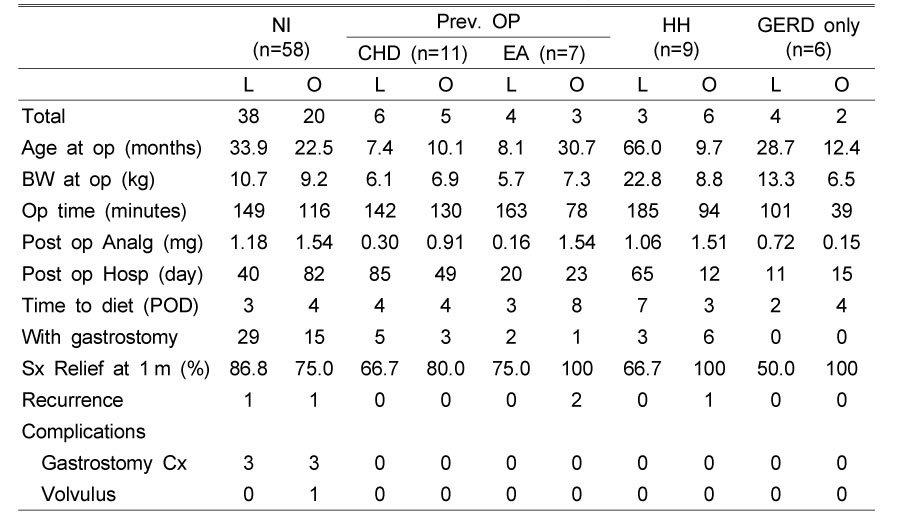
Abbreviations: NI; neurologic impairment, Prev. OP; previous operation, HH; Hiatal hernia, GERD; gastroesophageal reflux disease, CHD; congenital heart disease, EA; esophageal atresia, L; laparoscopy, O; open surgery, op; operation, BW; body weight, Analg; analgesics, Hosp; Hospital stay, POD; postoperative day, Sx; symptom, Cx; complication.
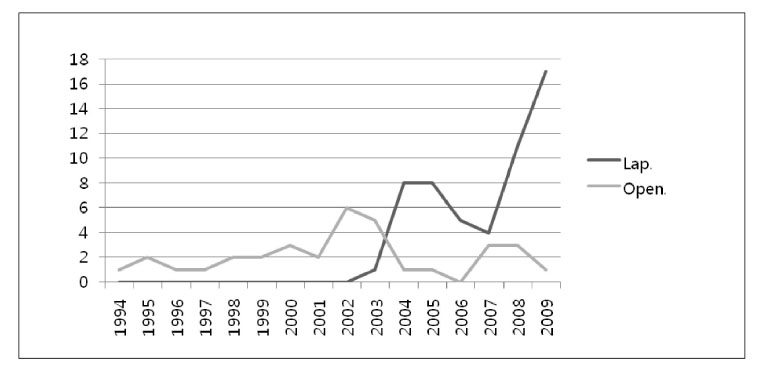
The Demographic Findings of Patients
(P value: Student T test and Pearson Chi-square)
Postoperative Result of Laparoscopic versus Open Fundoplication
(P-value: Fisher's Exact Test)
*Cause of Re-operation (Gastrostomy problem/Recurrence/Other problems)
Comparison of the Postoperative Results Considering Underlying Diseases
Abbreviations: NI; neurologic impairment, Prev. OP; previous operation, HH; Hiatal hernia, GERD; gastroesophageal reflux disease, CHD; congenital heart disease, EA; esophageal atresia, L; laparoscopy, O; open surgery, op; operation, BW; body weight, Analg; analgesics, Hosp; Hospital stay, POD; postoperative day, Sx; symptom, Cx; complication.
(P value: Student T test and Pearson Chi-square)
(P-value: Fisher's Exact Test)
*Cause of Re-operation (Gastrostomy problem/Recurrence/Other problems)
Abbreviations: NI; neurologic impairment, Prev. OP; previous operation, HH; Hiatal hernia, GERD; gastroesophageal reflux disease, CHD; congenital heart disease, EA; esophageal atresia, L; laparoscopy, O; open surgery, op; operation, BW; body weight, Analg; analgesics, Hosp; Hospital stay, POD; postoperative day, Sx; symptom, Cx; complication.