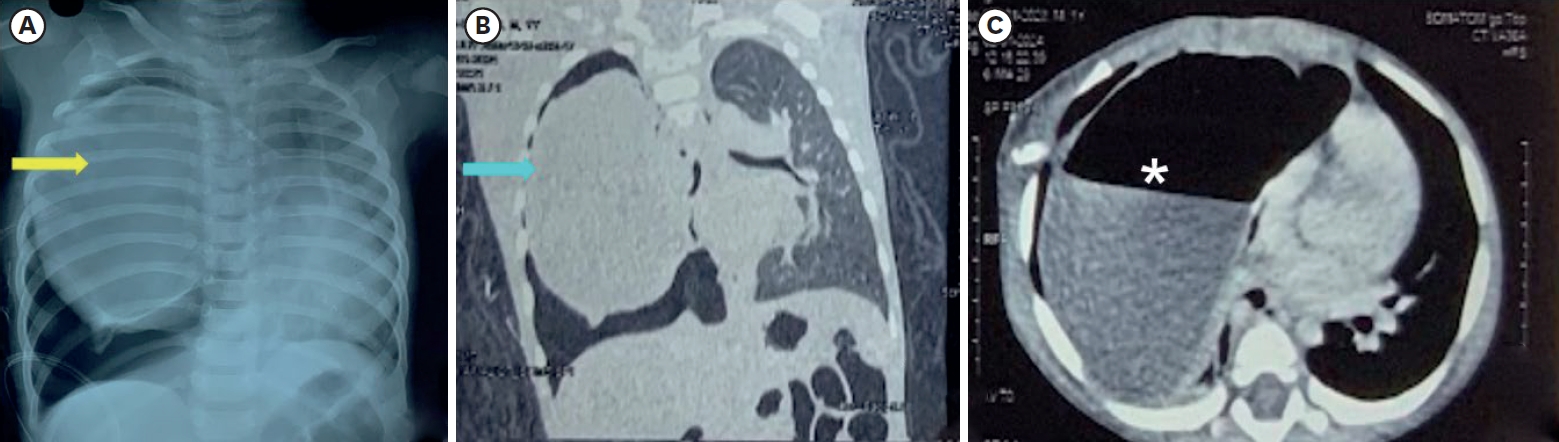
Congenital absence/hypoplasia/fusion of ribs are very rare anomalies and presentation varies from asymptomatic to life-threatening. Visibly evident cases are straightforward to diagnose but this is not always the case. Familiarity and awareness of these anomalies can help to diagnose cases with subtle signs and symptoms. Proper radiological investigations are vital for anatomical delineation. Absence or hypoplasia of the inferior ribs along with its attached muscles can cause ‘lung hernia’ that produces an unstable chest leading to paradoxical respiratory movements. Here, we present a case of hypoplastic and fused ribs in an infant, who presented with respiratory distress and created a diagnostic dilemma.
Citations

The introduction of Malone antegrade continence enema) in the management of children with fecal incontinence has brought remarkable improvement in patient care, Malone originally described appendix as a conduit and it has become widely accepted. However, surgeons are faced with situations where appendix is not available, the selection and creation of other conduit is always a challenge. We present our technique and experience with the use of alternative catheterizable conduits for antegrade continence enema (ACE).
Retrospective review of children who underwent ACE procedure in our institution from March 2009 to January 2014. The details retrieved: indication, reason for non availability of appendix, type of conduit, complications and patient's satisfaction.
Five children were identified in whom the appendix was not available or suitable. In four children cecal/colon-based flap was used and in one child, ileal (Monti) segment was used to create a conduit. The mean follow-up was 3.2 years. All patients were satisfied with the procedure and no stenosis or loss of conduit was noted in the follow-up.
Continent catheterizable conduit for ACE can be accomplished with transverse tubularized intestinal segments and cecal/colonic flaps, with excellent outcome, irrespective of tissue used. Surgeon's preference and the patient's peculiar anatomy should determine the surgical technique to be used.

