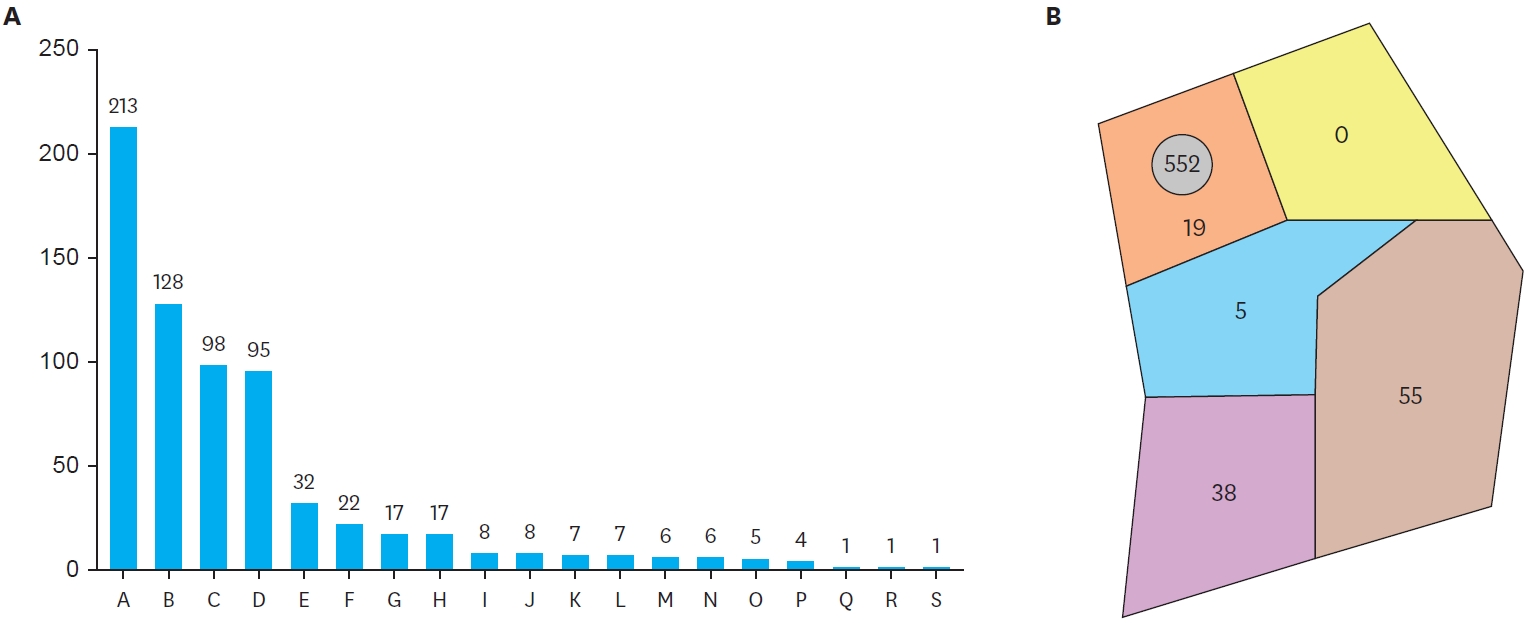
Tracheoesophageal fistula without esophageal atresia (H-type TEF) is a congenital anomaly that is characterized by a fistula between the posterior wall of the trachea and the anterior wall of the esophagus, not accompanied by esophageal atresia. The purpose of this study is to investigate the clinical characteristics, diagnostic time, the side of cervical approach and short term result after surgery by searching medical records of patients treated for H-type TEF. The search was done at University of Ulsan, Department of Pediatric Surgery of Asan Medical Center, and the total number of patients from May 1989 to December 2010 was 9 with M:F ratio of 1:2. The median gestational age was 39(+6) (32(+6)~41(+0)) wks. Seven out of nine patients were born at term and the other two were born premature. The clinical presentation was aspiration pneumonia, difficulty in feeding, chronic cough, vomiting, abdominal distension and growth retardation. The symptoms presented right after birth. The diagnosis was made with esophagography and the median time of diagnosis was 52 days of life. The majority of surgical corrections were performed within two weeks of diagnosis (median; 15d, range; 1d - 6m). Six patients had associated anomalies, and cardiac anomalies were most common. The cervical approach was utilized in all cases (right 2, left 7). Transient vocal cord palsy and minor esophageal leakage complicated two cases. Although the diagnosis of H-type TEF was difficult and often delayed, we had a good short term result. The left cervical approach was preferred.
Citations

Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has been utilized in congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) patients with severe respiratory failure unresponsive to conventional medical treatment. We retrospectively reviewed 12 CDH patients who were treated using ECMO in our center between April 2008 and February 2011. The pre ECMO and on ECMO variables analyzed included gestational age, sex, birth weight, age at the time of ECMO cannulation, arterial blood gas analysis results, CDH location, timing of CDH repair operation, complications and survival. There were 9 boys and 3 girls. All patients were prenatally diagnosed. Mean gestational age was 38.8 ± 1.7 weeks and mean birth weight was 3031 ± 499 gram. Mean age at the time of ECMO cannulation was 29.9 ± 28.9 hours. There were 4 patients who survived. Survivors showed higher 5 min Apgar scores (8.25 ± 0.96 vs. 7.00 ± 1.20,
Citations

Meckel's diverticulum (MD) has various clinical presentations and due to the limitation of imaging studies, pre-operative diagnosis is a challenge in pediatric patients. Recently, laparoscopic exploration has been suggested as a favorable method for the diagnosis and treatment of complicated MD. We investigated the results of laparoscopic-assisted surgery compared with open technique. We retrospectively studied patients who underwent resection of complicated MD at our institute from 1997 to 2010 and compared 11 treated by laparoscopic-assisted diverticulectomy (LD) with 11 treated by open diverticulectomy (OD) for complicated MD. Operation time was not significantly different in the two groups. Hospital stay and time to diet were not significantly different. Two patients were re-admitted due to mechanical ileus in the LD group. None of patients in either group needed re-operation. Considering the possibility of false-positive results with imaging studies and the cosmetic benefit, laparoscopic-assisted surgery is a safe and effective treatment modality to diagnose and treat complicated Meckel's diverticulum.
Citations

Pulmonary sequestration (PS) is a rare congenital malformation of the lower respiratory tract. The anomaly is characterized by absence of communication with the tracheobronchial tree and isolated blood supply from an anomalous systemic vessels. With the utilization of antenatal ultrasound, the diagnosis of asymptomatic neonatal PS has increased. Treatment options include observation, arterial embolization and surgical resection. The aim of the present study is to review the clinical course of PS and to share our experience with thoracoscopic resection. A total of 96 patients with PS were treated at Asan Children's Hospital between 1999 and 2010. The diagnosis of PS was established by CT in the cases managed by observation or embolization, and by tissue pathology in the surgical cases. Medical records and radiographic images were retrospectively reviewed. Thirty-nine patients were managed by embolization and 30 patients by surgery. The remaining 27 patients have been under observation without any procedures. Among 27 observation patients, 1 patient regressed completely and 10 patients were lost to follow up. Of the 39 embolizations patients, 2 had their lesion regress and sepsis was suspected after embolization. In 1 patient, the microcoil migrated to the iliac artery during the embolization procedure, and another patient developed renal abscess caused by renal artery embolization. Among 30 surgical cases, resection by thoracotomy was performed in 27 at the Department of Thoracic Surgery, and thoracoscopic resection in 3 at the Division of Pediatric Sugery. Only one wound complication ocurred. We conclud that surgical excision should be recommended for pulmonary sequestration, whether the sequestration is symptomatic or not because of the risk of infection, the low rate of natural regress, poor compliance, severe complications after embolization, and to exclude other pathology. In summary, thoracoscopic resection of the pulmonary sequestration is feasible, efficacious, safe and cosmetically superior even in neonatal period.

