Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a rarely occurring disease in the pediatric population. We report our center's experience of management of HCC in children and adolescents.
From 1996 to 2012, 16 patients aged 18 or younger were diagnosed with HCC at our center. The medical records of these 16 patients were retrospectively reviewed.
There were 9 boys and 7 girls. Median age at diagnosis of HCC was 14.5 years. All patient had pathologically confirmed diagnosis of HCC. Three patients had distant metastasis at the time of HCC diagnosis. Eight patients were surgically managed, including 4 liver resections, 3 liver transplantations, and 1 intraoperative radiofrequency ablation. The remaining 8 patients received systemic chemotherapy. Overall, 6 patients are alive at median 63.6 months after diagnosis of HCC. All survivors were surgically managed patients.
HCC is a rare disease occurring in childhood. Patients with systemic disease have poor outcome. Liver transplantation may be a good option for treatment of pediatric HCC.
Pediatric liver transplantation has evolved into a definite and effective therapeutic modality for various liver diseases in the pediatric patient. During the last 25 years, liver transplant outcomes in Korea have reached international standards and Korea has become the leader in living-donor liver transplantation. This review will present the cumulative outcomes of pediatric liver transplantation performed in Korea and will focus on other issues of interest involving pediatric liver transplant recipients, especially in the field of immunosuppression and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease.
Citations

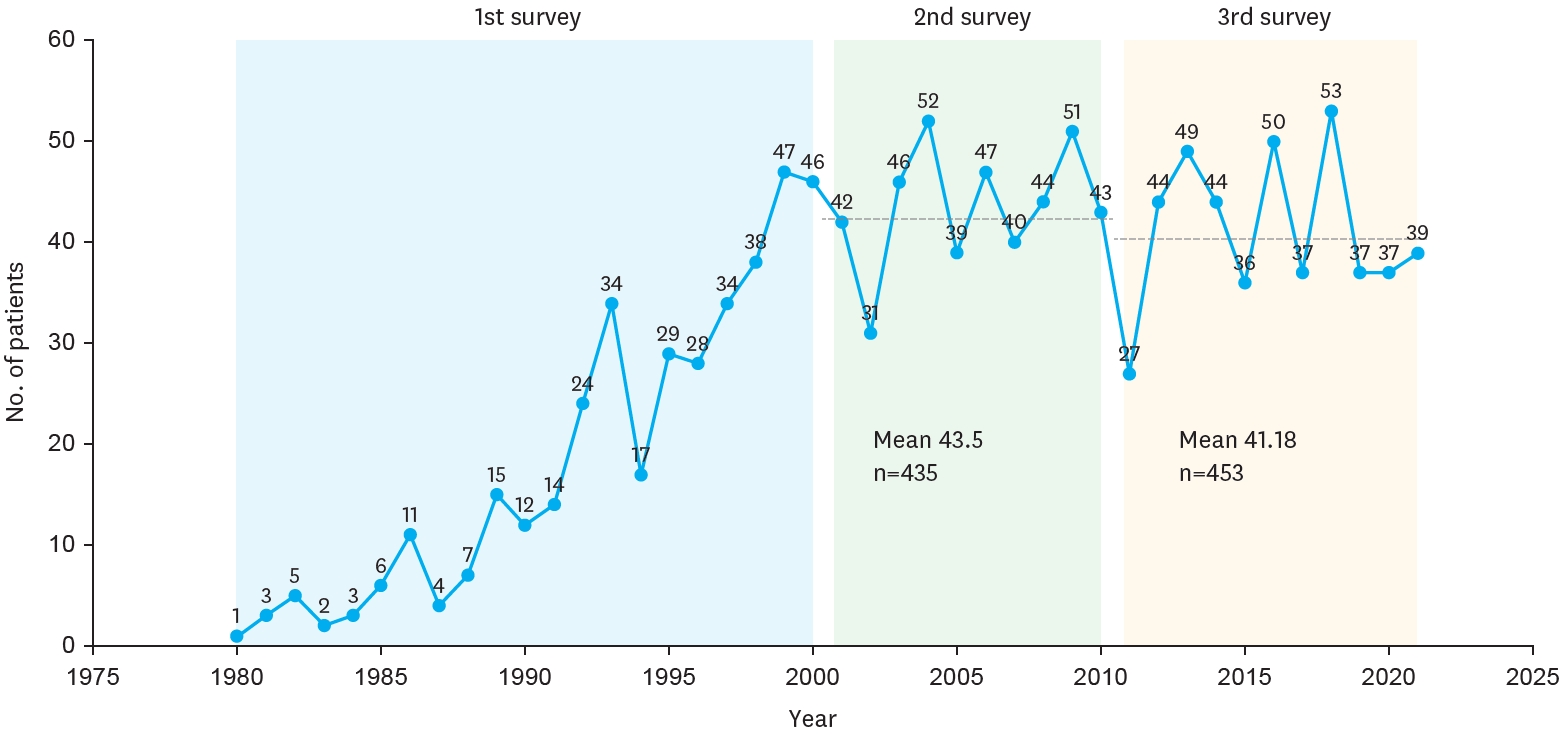
The Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons (KAPS) performed the second nationwide survey on biliary atresia in 2011. It was a follow-up study to the first survey, which was performed in 2001 for the retrospective analysis of biliary atresia between 1980 and 2000. In the second survey, the authors reviewed and analyzed the clinical data of patients who were treated for biliary atresia by the members of KAPS from 2001 to 2010. A total of 459 patients were registered. Among them, 435 patients primarily underwent the Kasai operation. The mean age of patients who underwent the Kasai operation was 66.2±28.7 days, and 89.7% of those patients had type III biliary atresia. Only five patients (1.4%) had complications related to the Kasai operation. After the Kasai operation, 269 (61.8%) of the patients were re-admitted because of cholangitis (79.9%) and varices (20.4%). One hundred and fifty-nine (36.6%) of the patients who underwent the Kasai operation subsequently underwent liver transplantation. The most common cause of subsequent liver transplantation was persistent hyperbilirubinemia. The mean interval between the Kasai operation and liver transplantation was 1.1±1.3 years. Overall the 10-year survival rate after the Kasai operation was 92.9% and the 10-year native liver survival rate was 59.8%. We had 23 patients for primary liver transplantation without the Kasai operation. The mean age patients who underwent primary liver transplantation was 8.6±2.9 months. In summary, among the 458 Kasai-operation and liver-transplantation patients, 373 lived, 31 died, and 54 were unavailable for follow up. One-third of the patient who survived have had complications correlated with biliary atresia. In comparison with the first survey, this study showed a higher survival rate and a greater number of liver transplantation.
Citations

Biliary atresia (BA) is an infantile cholestatic disease of progressive obliterative cholangiopathy with varying degrees of damage to both extra and intrahepatic bile ducts due to unknown causes. The diagnostic studies should be done to diagnose or exclude BA without unnecessary delay. Kasai portoenterostomy is the first choice of treatment for bile drainage from microscopic bile ductules present in the portal fibrous mass. The medical management after Kasai portoenterostomy should be done carefully to maintain bile excretion and prevent and treat complications including cholangitis, hepatic fibrosis, portal hypertension and nutritional problem. The reported five years-survival rates after Kasai portoenterostomy range from 30 to 60%. About 20% of all patients undergoing Kasai portoenterostomy during infancy survive into adulthood with their native liver. Even if Kasai portoenterostomy remains as the first line of treatment in BA, liver transplantation serves as a good salvage treatment when portoenterostomy fails or liver function gradually deteriorates after initially successful establishment of bile flow. Overall 5-year survival rate in BA is about 90% in recent series.

