Santulli enterostomy has been used for various surgical abdominal conditions that require temporary diversion of bowel during a neonatal period. The aim of this study was to report clinical outcomes of Santulli enterostomy and to evaluate its usefulness.
Between January 2000 and December 2016, 40 neonates who underwent Santulli enterostomy were enrolled; Santulli enterostomies were performed for 25 patients without previous laparotomy (primary Santulli group) and 15 patients with previous laparotomy (secondary Santulli group).
Small bowel atresia is the first common indication of Santulli enterostomy (22/40, 55.0%), and luminal discrepancy between proximal and distal bowel was the most common determinant factor of Santulli enterostomy (17/40, 42.5%). The median age at surgery and mean birth weight were 2 days and 2,480 g respectively in the primary group, and 71 days, 2,340 g respectively in the secondary group. Operation time was significantly longer in the secondary group than the primary group (156±48 minutes vs. 224±95 minutes, p=0.019), and there was no difference in the time taken to initiation of oral feeding between the two groups. Santulli enterostomy closure was performed at median 65 days after Santulli enterostomy for primary group and 70 days for secondary group. Six complications (15.0%) were found after Santulli enterostomy, and nine complications (24.3%) after Santulli enterostomy closure (p=0.302). The incidence of complications was significantly higher in secondary group than in primary group (4.5% vs. 53.3%, p=0.001), and the reoperation rate was also significantly higher in the secondary group (4.5% vs. 46.7%, p=0.004).
Santulli enterostomy could be applied as a temporary enterostomy in neonatal patients with various surgical abdominal diseases. Considering the high complication rate after secondary Santulli enterostomy closure, decision making on the timing of enterostomy closure should be done with caution.
Citations

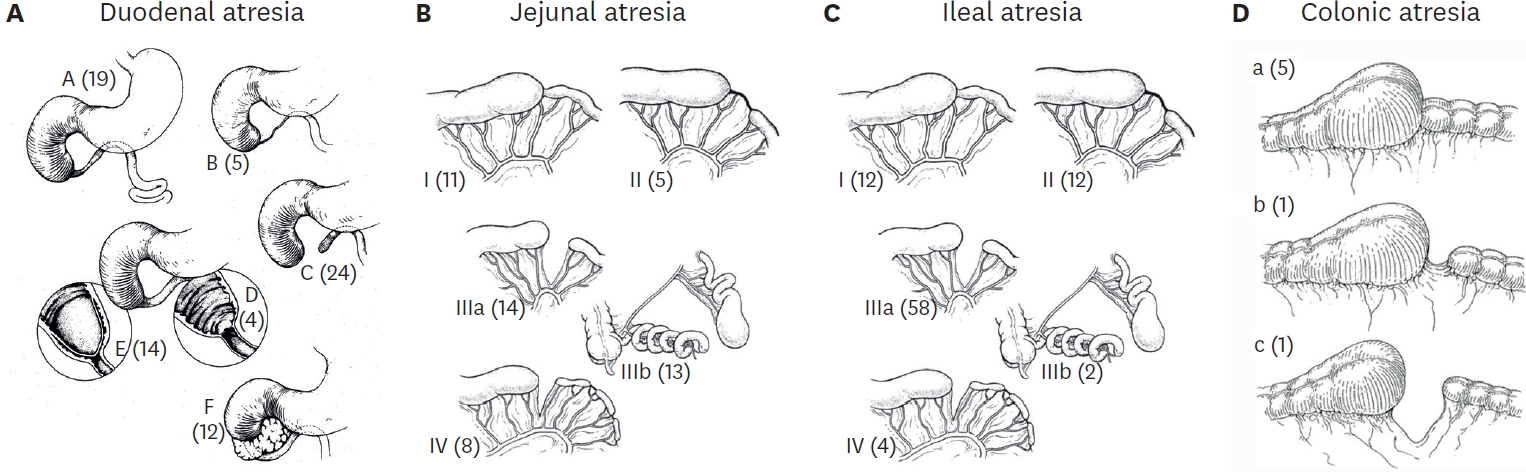
The members of the Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons conducted a retrospective study of two hundred and twenty-two cases of intestinal atresia for the period from January 1, 2007 to December 31, 2009. Seventeen hospitals were involved. There were 76 duodenal, 65 jejunal, and 81 ileal atresias (3 colonic). The male to female ratio was 0.85:1 in DA and 1.34:1 in JIA. Ninety-four patients(43.3%) were premature babies (DA 40.3%, JA 64.6%, IA 28.8%), and 70 babies (32.0%) had low birth weight (DA 38.7%, JA 44.4%, IA 16.0%). Antenatal diagnosis was made in 153 cases (68.9%). However, 27 infants (17.6%) with antenatal diagnosis were transferred to the pediatric surgeon's hospitals after delivery. Maternal polyhydramnios was observed in 81 cases (36.59%) and most frequent with proximal obstruction. In forty-four cases (19.8%), only simple abdominal film was taken for diagnostic study. The associated malformations were more frequently observed in DA - 61.8% in DA and 22.6% in JIA. Meconium peritonitis, small bowel volvulus and intussusception were more frequently associated with ileal atresia. The overall mortality rate was 3.6%.
Citations

Tapering enteroplasty was first described by Thomas in 1969 as one method of intestinal anastomosis. The advantages of tapering enteroplasty in the intestinal atresia are: First, it makes end-to-end anastomosis possible between the atretic bowel ends with considerable differences in diameters. Second, it promotes the recover of the postoperative bowel function. Third, it prevents the possibility of the short bowel syndrome by eliminating the need of resecting the dilated bowel. A total of 22 patients with intestinal atresia who underwent tapering enteroplasty from January 1988 to December 2005 at our institute were reviewed. In 3 of 22 cases, tapering enteroplasty was the 2nd operation after an initial end-to-oblique anastomosis. We reviewed the following items: age, sex, type and location of intestinal atresia, initial feeding and total enteral feeding start day, the length of hospital stay and complications. The average age of the patients was 7 days. Male to female ratio was 1 to 1.2 (10 cases: 12 cases). We performed the tapering enteroplasty on all types and locations of the intestinal atresia from the duodenum to the colon: type I (n=3), type II (n=4), type IIIA (n=7), type IIIB (n=5), type IIIB and IV (n=1), type IV (n=1) and type C (duodenum) and type IIIB and IV (jejunum). On the average, the oral feeds were started on the postoperative 8.8th day, and full caloric intake via the enteric route was achieved on postoperative 13.3th day. The average length of hospital stay was 19.6 days. There were 1 case (4.5 %) of anastomotic complication and 2 cases (9 %) of adhesive ileus among 22 patients. The tapering enteroplasty on all types of intestinal atresia is a usefull operative method when there are considerable diameter differences between the atretic bowel ends.
Citations

A survey on intestinal atresia was made among 34 members of Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons about the patients who were treated from the January 1, 1994 to December 31, 1996. The response rate was 82.4%. Two hundred and fifteen patients were analyzed. The lesion occurred in 73 cases at duodenum, in 72 cases at jejunum, in 71 cases at ileum and 2 cases at cecum and sigmoid colon each. There were 2 cases of combined anomalies (DA + JA + IA and DA + JA). Male to female ratio was 1:1 in duodenal atresia. and 1.8:1 in jejunoileal atresia. Seventy-four cases (34.3%) were premature babies (DA 35.2%, JA:48.6%, IA:19.2%), and 62 cases (28.7%) had low birth weight (DA:39.4%, JA 33.0%, IA:13.7%). Antenatal diagnosis was made in 92 cases (43.6%). However 22 cases (23.9%) of them were transferred to pediatric surgeon after delivery. Maternal polyhydramnios was observed in 63 cases (28.9%). Seventy-five cases (34.4%) were taken only simple abdominal film for diagnostic studies. The associated malformations were observed in 54 cases (24.8%) of intestinal aresia and more frequently observed in duodenal atresia (35 cases, 47.9%). Meconium peritonitis due to intrauterine bowel perforation was more frequently associated with ileal atresia compared to duodenum and jejunum. The overall mortality rate was 30%. (Abbreviations: DA;duodenal atersia, JA;jejunal atresia, IA;ileal atrsia, PT;p-value in total, PDJ,DI,JI;p-value between two groups among duodenal, jejunal and ileal groups)
Citations

Seventy neonates with congenital intestinal atresia and stenosis who were treated at pediatric surgical service, Hanyang University Hospital from September 1979 to December 1996 were analyzed retrospectively. The lesion occurred in 27 cases at the duodenum, in 26 cases at the jejunum, in 13 cases at the ileum and in 2 cases at the pylorus and colon each. There were 10 multiple atresias and 7 apple-peel anomaly cases. The atresia predominated over the stenosis by the ratio of 4 : 1. Male to female ratio was 1.3 : 1. The average gestational age was 38 weeks, and the average birth weight was 2,754 grams. Though 22.9 % were borne prematurely and 34.3 % had low birth weight, 92.3 % of them had a weight appropriate for gestational age. Polyhydramnios(40 %) was more frequently observed in duodenal and jejunal atresia while microcolon in ileal atresia(58.3 %). Weight loss and electrolyte imbalance occurred more frequently in the duodenal stenosis cases because of delayed diagnosis. Twenty(55.6 %) of 37 jejunoileal atresia cases had evidence of intrauterine vascular accident: 4 intrauterine intussusception, 3 intrauterine volvulus and 3 strangulated intestine in gastroschisis, and 10 cases of intrauterine peritonitis. There were one or more associated anomalies in 45 patients(64.3 %). Preoperatively proximal loop volvulus developed in 3 cases and proximal loop perforation in 5 cases and one case each of distal loop perforation, duodenal perforation and midgllt volvulus occurred in the jejunoileal atresia. Overall mortality rate was 20 %.
Citations


